Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
2
-dependent manner but also in the absence of O
2
(Fig. 8.9), leading to the hypothesis
that while this process may prevent H
2
S toxicity of cytochrome oxidase, it may also pro-
vide electrons and protons for oxidative phosphorylation, thus perhaps sparing carbohy-
drates for other use [5]. Under air-equilibrated conditions, mitochondrial H
2
S consumption
was accompanied by simultaneous increased O
2
consumption, leading some investigators
to use H
2
S-stimulated O
2
consumption as an indirect and largely qualitative measure of
H
2
S consumption. Using the PHSS to measure H
2
S consumption directly in combina-
tion with O
2
consumption provided a dynamic metabolic stoichiometry of H
2
S to O
2
con-
sumption over a range of O
2
levels as well as demonstrated that H
2
S can be consumed in
the absence of O
2
. This detailed assessment of mitochondrial H
2
S metabolism provided
evidence of specifi c enzymatic steps and insight into mammalian H
2
S metabolism.
8.6.2.2 Cultured cells, intact tissues and organs
To determine cellular H
2
S consumption rates, bolus additions of known H
2
S concentra-
tions were added to the respirometer chamber with or without rat aorta smooth muscle
12.5
m sulfide
(a)
8
15
6
10
4
5
2
0
0
10
10
(b)
8
8
6
6
4
4
2
2
0
0
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
Time, min
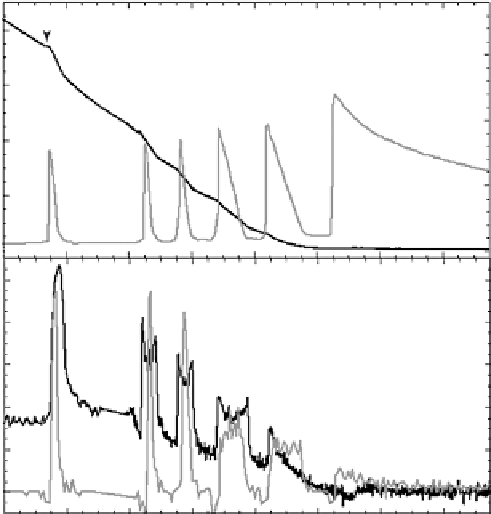
FIGURE 8.9
Mitochondrial O
2
and H
2
S consumption from non-limiting O
2
to anoxic conditions. (a)
Isolated mitochondria were exposed to repeated bouts of 12.5 µM H
2
S until anoxia was achieved. (b) At
higher O
2
levels, both O
2
and H
2
S consumption events are coincident, but as the O
2
levels decline the events
become uncoupled and O
2
consumption is limited fi rst. The multiphasic kinetics of O
2
consumption may
result from transient inhibition of cytochrome
c
oxidase by H
2
S. Under anoxia, H
2
S consumption continues
at a low level (after [36]; reproduced with permission of the Company of Biologists).













Search WWH ::

Custom Search