Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
surface of a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) was modifi ed fi rst with streptavidin.
The immobilized streptavidin was used to bind biotinylated anti-rabbit IgG. The modi-
fi ed surface was then exposed to rabbit IgG and rabbit IgG that had been labeled with the
enzyme alkaline phosphatase (AP). These two antibodies compete for a limited number
of binding sites of the immobilized anti-rabbit IgG and the square wave voltammetric
signal produced is due to the oxidation of the product of an enzymatic reaction. A detec-
tion limit (based on the analytical signal that is three times greater than the blank signal)
of 50 pmol L
1
(or 7.0 ng mL
1
) for rabbit IgG was achieved by this system.
(a)
(b)
labeled
signal
antibody
labeled
analyte
analyte
capture antibody
solid phase
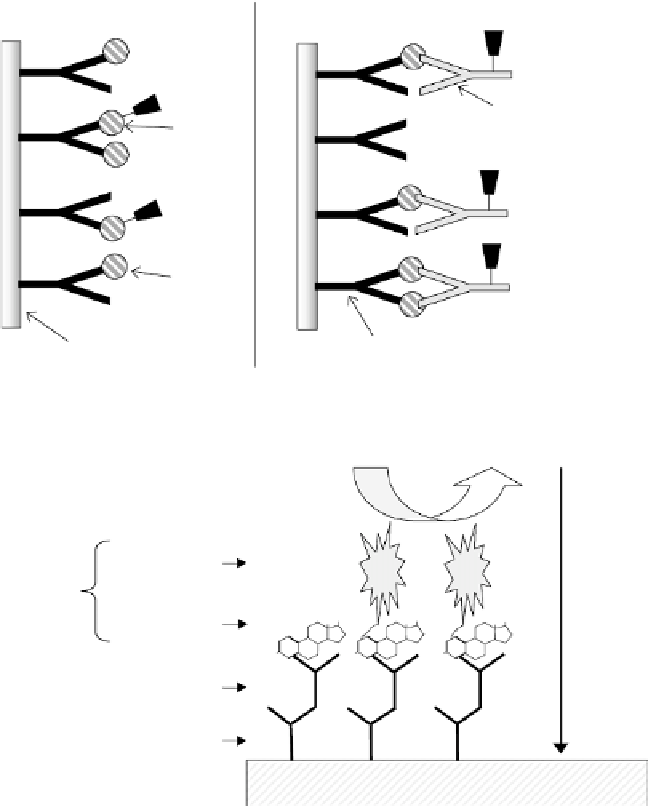
FIGURE 5.2
Schematic representation of (a) competitive and (b) non-competitive immunoassay formats.
1-naphthol
1-NP
Alkaline
phosphatase
ALP
ALP
e
Conjugate
electrochemical
measurement
OH
OH
OH
Estradiol
HO
HO
HO
Mouse anti-estradiol mAb
Rb anti-mouse lgG
Solid Phase
FIGURE 5.3
A schematic illustrating a competitive immunoassay format used for the detection of estra-
diol. (Reprinted from [11] with permission from Elsevier.)





Search WWH ::

Custom Search