Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
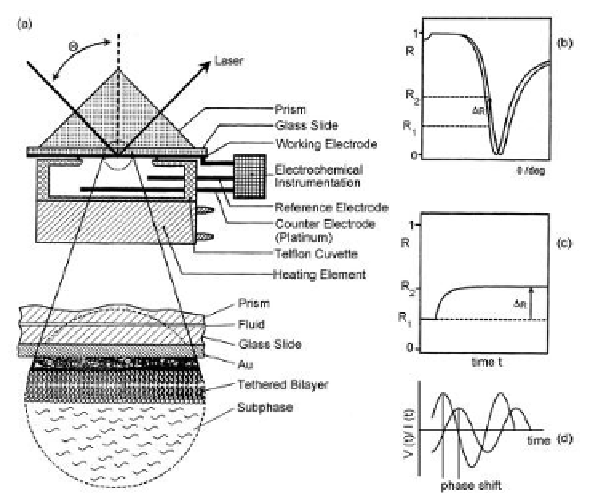
The angular position of the minimum of the SPR reflectivity
curves (i.e., the curves of reflectivity versus incident angle; see
Fig. 7b
) is critically dependent on the thickness of the layer ad-
sorbed on the support surface. When macromolecules assemble
Figure 7. (a) Experimental set-up for surface plasmon resonance measurements,
combined with an EIS module for simultaneous SPR and electrochemical meas-
urements on tBLMs. The enlargement shows the solid/solution interface with the
thin Au layer used for surface plasmon excitation, and the tethered lipid bilayer in
contact with the aqueous phase; (b) typical SPR reflectivity curves before and after
the formation of the distal lipid monolayer (on top of the self-assembled proximal
tethered lipid monolayer) by vesicle fusion; (c) kinetics of the fusion process rec-
orded by monitoring the change of reflectivity at a fixed angle of incidence as a
function of time; (d) time dependence of the small-amplitude a.c. voltage used in
EIS measurements and of the resulting a.c. current of equal frequency and different
phase angle. (Reprinted from Ref.
9b
with kind permission from Elsevier.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search