Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
5.6.3 Numerical Assessments
In the numerical analysis, three cases are considered. The axial force is
assumed to be
P
= 1.0 kN in all cases.
5.6.3.1 Effect of Pin Size on Bone Remodeling
To study the relationship between pin size and bone porosity, three sizes of
the pin δ/
a
are considered: δ/
a
= 3%, 5%, and 6%. The Young's modulus of the
pin is
E
= 150 GPa. Figure 5.19 shows the results of bone porosity as a func-
tion of
t
for the three sizes of the pin above.
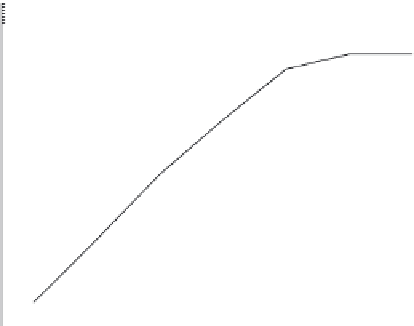
Figure 5.20 shows the effect of pin size on bone surface remodeling. It can
be seen from Figures 5.19 and 5.20 that the pin size has a significant effect
on the bone remodeling process. When the pin size is relatively small—say,
δ/
a
= 3%—bone porosity increases significantly (or bone density decreases)
along with an increase in the remodeling time. The explanation for this is
as follows. When the pin size is small, the contact force between bone tissue
and the pin is also relatively small, which causes the bone to be in a state
of near disuse. Then the value of internal growth factors may be smaller
than the threshold value, activating the remodeling process for the bone tis-
sues that are in disuse. This process leads to an increase in bone porosity
and in the inner radius of the bone. However, when the pin size increases to
δ/
a
= 5% or above, the bone porosity seems to be kept in a constant state as
time progresses. The change in the inner radius of the bone is slowed down
significantly. Perhaps the contact force between the pin and the bone just
causes the bone growth factor to be in a state of equilibrium.
δ/
a
= 3%
δ/
a
= 5%
δ/
a
= 6%
0.25
0.20
0.15
0.10
0.05
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
t
(day)
FIGURE 5.19
Bone porosity versus time
t
for three sizes of pin.