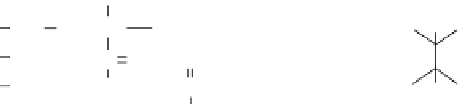Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
UV
+
C
OH
O
CH
3
PDMS
Benzophenone
CH
3
OH
CH
2
(CH
2
-C)
n
+
CH
3
CH
3
O
C O
O-(CH
2
)
2
-OPO-(CH
2
)
2
-N
+
(CH
3
)
3
OH
O
-
PDMS-g-poly(MPC)
Benzopinacol
Figure 15.2
Scheme. of. the. UV-induced. free. radical. surface. graft. polymerization. onto. a. PDMS. surface.. (Reprinted. from.
Biomaterials
,. 27,. . Goda,. T.,. . Konno,. T.,. . Takai,. T.,. Moro,. M.,. and. Ishihara,. K.,. Biomimetic. phosphorylcholine.
polymer. grafting. from. polydimethylsiloxane. surface. using. photo-induced. polymerization,. 5151-5160,. 2006..
Copyright.(2006),.with.permission.from.Elsevier.)
(Goda.et.al..2006)..This.reaction.is.illustrated.in.Figure.15.2..This.enhanced.the.polymer.
surface.hydrophilicity,.anti-fouling.properties,.and.its.biocompatibility.
PDMS. is. a. classical. material. for. microluidic. devices. since. it. is. easily. molded. into. the.
various. shapes.. A. microchip. was. developed. using. PDMS. for. a. solid-phase. extraction.
device. (Karwa. et. al.. 2005).. Sorbent. particles. were. immobilized. onto. PDMS. microluidic.
channels.through.sol-gel.chemistry..The.PDMS.used.in.this.study.served.as.a.matrix.for.
the.sorbent.particles,.not.directly.for.the.solid-phase.extraction.
Cell-culture. devices. can. also. be. constructed. with. PDMS.. Three-dimensional. (3D). cell.
culture. has. become. a. very. important. area. of. research. for. biological. scientists. since. 3D.
cultures.better.represent.the.cells'.natural.growth.environment..The.biocompatibility.and.
ease.of.use.of.PDMS.make.it.ideal.for.this.application..In.a.study.conducted.by.Anada.et.al.,.
a.thin.PDMS.membrane.was.used.as.a.support.for.cell.culture..The.purpose.of.these.mem-
branes. was. to. create. spheroids. (multicellular. aggregates).. These. spheroids. were. formed.
through.deformation.of.the.membrane.through.decompression.(Anada.et.al..2010).
15.2.3.3 Chitin/Chitosan
Chitin. is. a. naturally. occurring. long-chain. polymer. composed. of.
N
-acetylglucosamine..
This.polymer.can.be.found.in.the.exoskeletons.of.crustaceans.and.insects.as.well.as.the.
cell. walls. of. fungi.. Chitosan. is. a. deacetylated. chitin. composed. of. randomly. distributed.
repeating. units. of.
N
-acetylglucosamine. linked. to. a. deacetylated. d-glucosamine. unit..
Both. chitin. and. chitosan. are. considered. glycosaminoglycans. (GAGs). and. have. unique.
properties,. which. make. them. interesting. for. research.. Chitin. is. not. soluble. in. aqueous.
media.while.chitosan.is.soluble.in.acidic.conditions.because.of.available.amino.groups.on.
d-glucosamine.that.can.be.protonated.(Aranaz.et.al..2009).
In.a.study.by.Fabela.Sánchez.et.al..(2009),.chitosan.was.cross-linked.with.glutaraldehyde.
for. mammalian. cell. culture.. The. purpose. was. to. create. a. substrate. that. more. closely.
resembles.the.extracellular.matrix.(ECM)..The.cross-linking.of.chitosan.with.glutaraldehyde.
causes.the.polymer.to.become.a.hydrogel..This.hydrogel.was.then.studied.for.its.use.as.