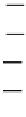Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Primary (1°)
G U
A
(a)
A A
U C C G G
Secondary (2°)
Canonical binding
A U
C G
G C
U A
Noncanonical
binding
G U
U G
I A
I C
I U
(b)
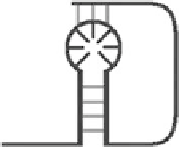
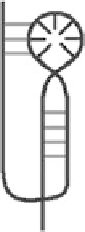
Hairpin
Bulge
Tertiary (3°)
(c)
Figure 5.1
(See companion CD for color igure.)
. RNA. conformations. at. different. structure. levels.. (a). RNA. sequences.
are. distinguished. from.DNA.primary. strands. by.the.presence. of.uracil.. (b).RNA.forms.canonical.base. pairs.
but.is.also.capable.of.creating.weaker.but.still.stable.base.pairs,.notably.the.G-U.pair.and.inosine.pairing.in.
tRNA..This.greater.binding.potential.and.structural.lexibility.leads.to.creation.of.hairpins.or.bulges,.resulting.
from.internal.binding..(c).Tertiary.structures.such.as.pseudoknots.have.important.biological.structures.but.are.
incredibly.dificult.to.predict.through.computer.modeling.
stability. of. G-quartets/quadruplexes,. which. are. primarily. Hoogsteen. bases. (Mori.
et. al.. 2004).. DNA. forms. the. more. famous. telomere. caps. that. are. made. of. G-quartets..
These.interactions.are.far.more.complicated.than.standard.base.pairing,.which.are.both.
harder.to.model.and.more.poorly.understood..However,.these.are.inherently.essential.
for.proper.functioning.of.RNA.in.biological.systems.
The. traditional. base. pairing. and. secondary. structure. of. RNA. is. most. commonly.
depicted.as.part.of.the.central.dogma,.where.RNA.acts.as.the.intermediate.step.between.
DNA.and.protein..However,.the.intricacy.of.RNA.base.pairing.also.allows.for.the.ability.
to. form. complex. tertiary. structures,. permitting. RNA. to. form. a. large. number. of. essen-
tial.functional.elements.in.the.cell,.beyond.its.usage.as.information.intermediate..One.of.
RNA's.best.known.examples.of.this.is.the.ribozyme,.in.which.the.tertiary.structure.of.the.
RNA. molecule. allows. for. catalysis. of. chemical. reactions,. giving. it. protein-like. qualities.
and.leading.to.the.theory.of.the.primordial.RNA.world.(Kruger.et.al..1982).