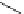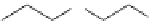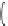Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
c
d
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
COOH
COOH
COOH
α
-carboxy-
ε
-caprolactone
β
-malic acid
α
-malic acid
O
R
O
e
f
R
1
O
O
H
carboxy lactic acid
N
O
O
O
R
2
O
R
1
:H, CH
3
OR
O
trimethylene carbonate derivative
depsipeptide
Fig. 3 Examples of monomer units having reactive side-chain groups, which can be
copolymerized with polyesters: (a)
a
-malic acid, (b)
b
-malic acid, (c)
a
-carboxyl-
e
-caprolactone,
(d) carboxy lactic acid, (e) trimethylene carbonate derivative, and (f) depsipeptide
polymer for macromolecular prodrugs for anticancer drugs was achieved by attach-
ment of anticancer drugs, 5-fluorouracil (5FU) and doxorubicin (DXR), utilizing the
reactivity of side-chain groups [
79
,
80
].
b
-PMA was also synthesized by ROP of
cyclic monomer [
81
] and its use as a drug carrier was also reported [
82
]. Kimura
reported the synthesis of poly(malic acid
-co-
lactide) and poly(malic acid-
co
-
glycolic acid) by ROP of 1:1 cyclic dimer of malic acid benzyl ester and lactic
acid or glycolic acid (Glc) [
83
,
84
]. They later reported the utility of the copolymer
as a biodegradable scaffold for tissue engineering, exhibiting high cell-adhesive
properties by immobilizing the cell-adhesive peptide arginine-glycine-aspartic acid
(RGD) [
85
].
Lavasanifar and coworkers reported PCL-like copolymers, poly(
a
-carboxyl-
e
-caprolactone), having reactive carboxylic acid side-chain groups [
86
,
87
]. They
reported the synthesis of block copolymers with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and
the use of the copolymers as micelle-forming reactive polymers for immobilizing
hydrophobic anticancer drugs [
88
]. Nottelet reported the synthesis of LA-like and
b
-propiolactone-like cyclic monomers from glutamic acid (Glu) and aspartic acid
(Asp), respectively, and the block copolymerization of them with LA [
89
]. Hedrick
et al. reported poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC)-like polymers bearing functional
carboxylate side chains [
90
-
92
]. They reported the preparation of PTMC block
copolymers immobilizing sugar units for DDS.
2.1.3 Polydepsipeptides
Copolymers of
a
-hydroxy acids and
a
-amino acids are one type of poly(ester-
amide)s and are called polydepsipeptides (PDPs) [
17
]. Since some of natural
occurring
a
-amino acids, typically Asp, Glu, lysine (Lys), cysteine (Cys), serine
(Ser), and threonine (Thr), possess reactive (hydrophilic) side-chain groups, PDPs