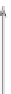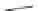Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Hydrophilic shell
~100nm
Hydrophobic segment
Hydrophilic segment
Hydrophobic core
water
self- assembly
polymer micelle
water
AB-type diblock copolymer
Inner water phase
~5
μ
m
Hydrophilic layer
Hydrophoibic layer
polymersome
Hydrophilic main chain
Hydrophobic group or chain
Hydrophobic domain
(physical cross linking
point)
water
~100nm
Hydrophilic domain
self-assembly
Graft copolymer
(hydrophilic main chain)
Nanogel
Fig. 1 Typical examples of nanometer-scale polymeric assemblies: polymermicelles, polymersomes,
and nanogels
it is extremely important to have precise control of intermolecular noncovalent
interactions such as hydrophobic interactions based on their molecular structures. In
fact, most such noncovalent assembly systems are made of amphiphilic copolymers.
Aliphatic polyesters are basically hydrophobic semicrystalline polymers having no
reactive functional groups. Many methods for adding hydrophilicity and functionality
to the aliphatic polyesters have been carried out by copolymerization with functional
monomers or hybridization with other functional hydrophilic polymers [
13
-
19
].
This chapter focuses on biodegradable polymers, mainly aliphatic polyesters, and
reviews the synthesis of amphiphilic biodegradable copolymers containing aliphatic
polyesters as components.Moreover, the application of various types of self-assembled
systems using amphiphilic biodegradable copolymers, such as micro- or nanosized
particles (MSs, NSs, polymer micelles, nanogels, and polymersomes), supramolecular
physically interlocked systems, and stimuli-responsive systems including physically
crosslinked hydrogels for biomedical use such as DDS are also reviewed.
2 Synthesis of Biodegradable Amphiphilic Polyesters
2.1 Homopolymers and Random Copolymers
2.1.1 Aliphatic Polyesters
So far, many studies have focused on the development and application of aliphatic
polyesters such as PLA [
1
-
3
], PGA [
41
,
42
], and PCL [
43
,
44
]. Figure
2
shows the
structures of their monomers: lactides (LAs), glycolide (GA),
e
-caprolactone (CL),
and some typical comonomers.