Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
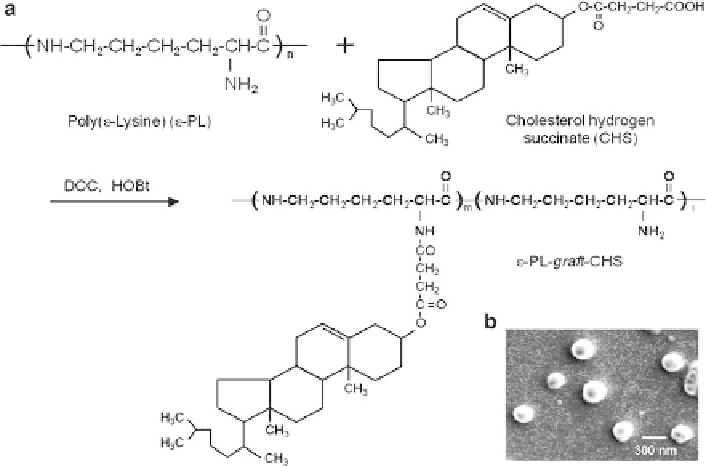
Fig. 7 (a) Synthesis of amphiphilic
e
-PL-
graft
-cholesterol hydrogen succinate (
e
-PL-CHS).
(b) SEM image of nanoparticles prepared from
e
-PL-CHS
a very safe material for use in humans. Therefore, the nanoparticles fabricated from
e
-PL may be useful for DNA vaccine delivery and adjuvants.
2.3 Amphiphilic Polysaccharide Nanoparticles
Polysaccharidic hydrogel particles have been often used for designing protein-
loaded systems for therapeutic applications. Polysaccharides are very hydrophilic
polymers, and their hydrogels thus exhibit a good biocompatibility. Various type
of hydrophobized polysaccharides, such as pullulan [
74
,
75
], curdlan [
76
], dex-
tran [
77
], alginic acid [
78
], and chitosan [
79
], have been used for preparation of
nanoparticles. Akiyoshi et al. reported that self-aggregated hydrogel nanoparticles
could be formed from cholesterol-bearing pullulan by an intra- and/or intermo-
lecular association in diluted aqueous solutions [
80
]. Recently, much attention has
been paid to chitosan as a drug or gene carrier because of its biocompatibility and
biodegradability. Chitosan is a polysaccharide constituted of
N
-glucosamine and
N
-acetyl-glucosamine units, in which the number of
N
-glucosamine units exceeds
50%. Chitosan can be degraded into nontoxic products in vivo, and thus has
been widely used in various biomedical applications [
81
,
82
]. Chitosan has
cationic characters even in neutral conditions to form complexes with negatively
charged pDNA. Jeong et al. prepared nanosized self-aggregates composed of