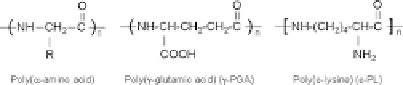Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
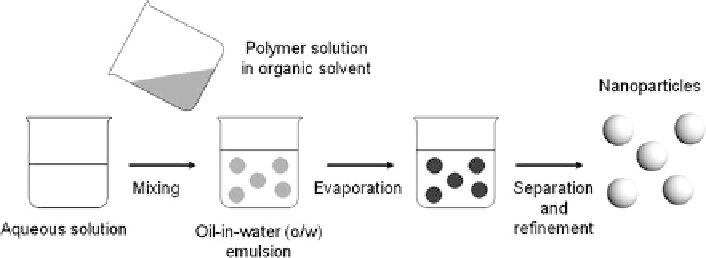
Fig. 3 Preparation of polymeric nanoparticles by emulsion solvent evaporation technique
Fig. 4 Chemical structures
of synthetic and naturally
occurring poly(amino acid)s
2.2 Amphiphilic Poly(amino acid) Nanoparticles
Recently, many studies have focused on self-assembled biodegradable nanoparticles
for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Nanoparticles fabricated by the
self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers or hydrophobically modified
polymers have been explored as drug carrier systems. In general, these amphiphilic
copolymers consisting of hydrophilic and hydrophobic segments are capable of
forming polymeric structures in aqueous solutions via hydrophobic interactions.
These self-assembled nanoparticles are composed of an inner core of hydrophobic
moieties and an outer shell of hydrophilic groups [
35
,
36
].
In particular, poly(amino acid)s have received considerable attention for their
medical applications as potential polymeric drug carriers. Several amphiphilic
block and graft copolymers based on poly(amino acid)s have been employed,
such as poly(
a
-
L
-glutamic acid) [
37
], poly(
g
-glutamic acid) [
38
], poly(
e
-lysine)
[
39
] (Fig.
4
), poly(
L
-aspartic acid) [
40
], poly(
L
-lysine) [
41
], poly(
L
-arginine) [
42
],
and poly(
L
-asparagine) [
43
] as hydrophilic segments, and poly(
b
-benzyl-
L
-aspartate)
[
44
], poly(
g
-benzyl-
L
-glutamate) [
45
], and poy(
L
-histidine) [
46
] as hydrophobic
segments. In general, amphiphilic copolymers based on poly(amino acid)s form
micelles through self-association in water.
Poly(
g
-glutamic acid) (
g
-PGA) is a naturally occurring poly(amino acid) that is
synthesized by certain strains of
Bacillus
[
47
]. The polymer is made of
D
- and
L
-glutamic acid units linked through the
a
-amino and the
g
-carboxylic acid groups,
and its
a
-carboxylate side chains can be chemically modified to introduce various
bioactive ligands, or to modulate the overall function of the polymer [
48
-
52
].
Unlike general poly(amino acid)s,
g
-PGA has unique characteristics of enzymatic
degradation and immunogenicity. It has been reported that
g
-PGA has resistance