Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
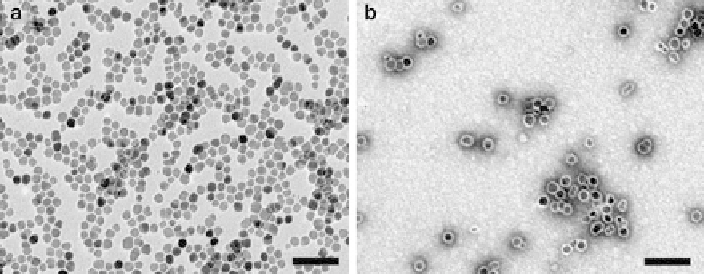
Fig. 21 TEM images of (a) as-synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles, (b) poly (amino acid)-coated
iron oxide nanoparticles in water.
Scale bars
: 80 nm (Adapted from[
79
])
behavior is a particular advantage in magnetic separation, one of the simplest
applications. Magnetic separation is now well established as a viable alternative
to centrifugal separation of complex chemical or biological solutions. Iron oxide
particles are first encased in a biocompatible coating to form tiny beads. TEM
images of some iron oxide nanoparticles are shown in Fig.
21
. The beads are then
“functionalized,” i.e., their surfaces are treated with a biological or chemical agent
known to bind to a specific target. On placing the beads in solution, any target cells
or molecules will latch onto the functionalized surfaces.
An alternative class of MNPs was produced from pure transition metals, such as
Fe, Ni, and Co, which exhibit ferromagnetic behavior. Unlike the SPIO and
ultrasmall SPIO (USPIO) particles, these pure metal particles retain their magneti-
zation once an external magnetic field is removed, causing particulate clustering.
Ferromagnetic nanoparticles also tend to have a larger magnetic moment than their
superparamagnetic counterparts. Ultrasmall Fe particles are, thus, likely to produce
a better signal in magnetic sensors or to respond more readily to an applied field
gradient than iron oxide particles of the same size. Upon conjugation with the
appropriate targeting molecules, MNPs can be utilized for the active detection of
cancer. The active targeting can be applicable in diagnosis as well as in therapeutics
for cancer [
80
], artherosclerosis etc.
6.5.1 Magnetite, Maghemite, and Ferrites
Synthesis of PEG-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles
PEG is hydrophilic and is widely used in biological research because it protects
surfaces from interacting with cells or proteins. Thus, coated particles may result in
increased blood circulation time. For their preparation, 10-mg magnetite particles
were dispersed in 1.0 mL of deoxygenated water by sonication for 30 min. The
aqueous dispersion of MNPs was dissolved in the aqueous cores of reverse micelles