Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
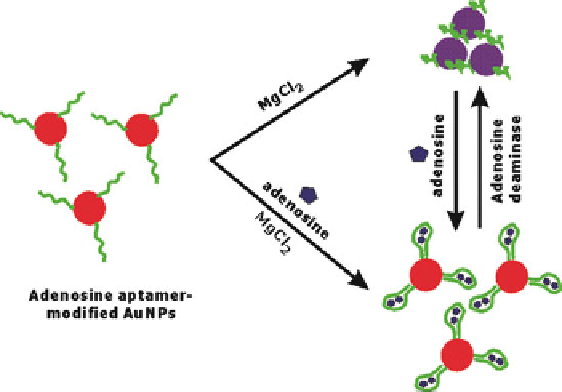
Fig. 9 Aptamers conjugated gold nanoparticles. (Adapted from [
49
])
and/or monitoring modalities can be based on traditional fluorophores, or QDs and
SPIONs. Aptamers are DNA or RNA oligonucleotides that fold by intramolecular
interaction into unique three-dimensional conformations capable of binding to
target antigens with high affinity and specificity. Aptamers are quickly emerging
as a new powerful class of ligands that rival antibodies in their potential for
diagnostic and therapeutic application.
Medley et al. have shown the use of aptamer-conjugated nanoparticles for cancer
cell detection [
50
]. Herr et al. [
51
] have shown the rapid collection and detection of
leukemia cells using a novel two-nanoparticle assay with aptamers as the molecular
recognition element.
6.1.4 Polymer-Modified Nanoparticles
Biocompatible or biodegradable polymers have been extensively explored in recent
years because of their potential biomedical applications, e.g., poly(lactic acid)
(PLA), poly(glycolic acid) (PGA), poly(lactic-
co
-glycolic acid) (PLGA), PEG,
alginate, etc. A multifunctional biodegradable PLGA nanoparticle attached to
moieties such as T-cell antibodies and contrast agents for MRI is shown in Fig.
10
.
PEG modification of nanoparticles increases circulation time by evading macro-
phage-mediated uptake and removal from the systemic circulation. Non-PEGylated
nanoparticles are quickly eliminated from the bloodstream because of the adsorp-
tion of blood proteins (opsonins) onto their surface, which triggers the recognition
of the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS) by the macrophages. Plasma half-life
(
t
1/2
) was less than 12 min for amphiphilic poly(acrylic) short chain (750 Da)
methoxy-PEG or long chain (3,400 Da) carboxy-PEG QDs. But, plasma
t
1/2
was