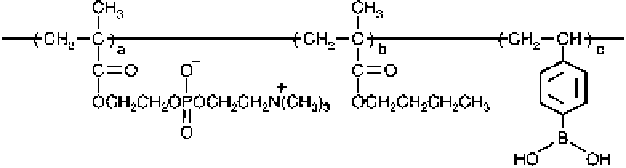Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
It is known that boronic acids can bind with hydroxyl compounds, including
polyols such as PVA, through the complex formation of a reversible covalent
bonding [
56
,
57
].
Using this property, a glucose-responsive hydrogel system to control release of
insulin has been prepared. The MPC polymer bearing a phenylboronic acid moiety,
poly[MPC-
co
-
n
-butyl methacrylate (BMA)-
co
-
p
-vinylphenylboronic acid (VPBA)]
(PMBV), can spontaneously form a hydrogel with PVA, even when the polymers
are dissolved in cell culture medium [
40
,
41
]. The PMBV/PVA hydrogel can be
dissociated by addition of low molecular weight sugar compounds based on the
exchange reaction with PVA.
PMBV was synthesized by a conventional radical polymerization. The monomer
unit compositions of the PMBV were 0.64, 0.25, and 0.11 unit mole fractions for
MPC, BMA, and VPBA, respectively. The number-averaged molecular weight and
weight-averaged molecular weight were 6.2
10
4
, respectively.
This PMBV was completely water-soluble due to hydrophilic MPC units in the
polymer. Figure
1
shows the chemical structure of PMBV.
When the PMBV solution and PVA solution were mixed, a hydrogel was formed
within a short term. Dissociation of the PMBV/PVA hydrogel occurred through
addition of a sugar compound such as
D
-sorbitol. This spontaneous gelation and
dissociation mechanism is useful for 3D cell immobilization, and the PMBV/PVA
hydrogel is a promising platform as a soft biodevice for 3D cell engineering. Figure
2
shows the concept of 3D cell engineering based on a PMBV/PVA hydrogel system.
The gelation mechanism is shown in Fig.
3
. The spontaneous gelation was
visually confirmed when the polymer concentration was 5 wt% PMBV solution
and 2.5 wt% PVA solution.
Figure
4
indicates the dynamic viscoelasticity of the PMBV/PVA hydrogel. The
dynamic viscoelasticity was measured immediately after mixing of the two polymer
solutions. It was confirmed that the cross-point between the storage modulus (G
0
)
and loss modulus (G
00
) is at 37 s. This result indicated that the mixture formed a
crosslinking network, and that the mixture finally produced a hydrogel structure.
Furthermore, gelation even occurred in the cell culture medium. Also, the hydrogel
was reversibly dissociated by the addition of sugar molecules. The hydrogel had
good network structure and the pore size was a few micrometers.
10
4
and 6.5
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of water-soluble poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine-
co
-
n
-butyl methacrylate-
co
-
p
-vinylphenylboronic acid (PMBV)