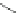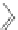Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
b
a
Fig. 23 (a) SEM image of cross-section of 10 wt% theophylline-loading XbOCL-10 film.
(b) Release profile of theophylline from (
filled circles
) XbOCL-10 and (
open circles
) XbOCL-
20 films in PBS at 37
C. Reprinted from [
328
] with permission
We reported the possibility of biodegradable SMPs as DDS devices [
330
].
We prepared crosslinked branched oligocaprolactone (XbOCL) exhibiting remark-
ably rapid temperature-responsive shape recovery within a small temperature change:
90% of the permanent shape was recovered upon heating to within a 2
C range
(37-39
C). The SMPs exhibited complete shape recovery from a temporary shape
to the permanent shape within 10 s at 42
C. We then chose theophylline as a
model drug and prepared theophylline-loaded (10 and 20 wt%) SMPs (Fig.
23
).
The theophylline-loaded SMPs showed high shape-memory effect, as did the
SMP without drug. A sustained release of the theophylline from the matrices was
achieved over 1 month without an initial burst-release in PBS at 37
C. A new type of
smart biomedical material could be demonstrated by combining shape-memory
effect with controlled drug release in a biodegradable SMP system.
9 Conclusion
In this chapter, the synthesis, preparation, and application of biodegradable polymeric
self-assembly systems, includingMSs, NSs, polymer micelles, nanogels, polymersomes,
supramolecular (interlocked) systems, and stimuli-responsive systems, have been
reviewed. There is no doubt that these polymeric assembly systems should play very
important roles in the next generation of nanomedicine. Although they exist in a
wide range of sizes from nano- to macroscales, it is extremely important to control
the intermolecular interactions for design of their assembled structures and final
functions. Biological systems use weak intermolecular interaction to maintain life.
So, more precise control of intermolecular interactions should lead to higher levels
of function, for example, by mimicking biological systems. Fine synthetic and
assembly methods for polymers should be the powerful and promising tools for
achieving precise design of polymers and their associated states. Although