Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
PEG-
b
-PLLA-
b
-PEG or eight-arm PEG-
b
-PDLA-
b
-PEG [
321
]. An aqueous solu-
tion of a 1:1 mixture of these copolymers was in sol state at room temperature, but
instantaneously formed a hydrogel in response to increasing temperature. The
resulting hydrogel exhibited a significantly higher storage modulus (ca. 10 kPa) at
37
C, twice that of the eight-arm PEG-
b
-PLLA-cholesterol system. Interestingly,
once formed at the transition temperature, the hydrogel was stable even after cooling
below the transition temperature. The hydrogel formation process was irreversible
because of the formation of stable SC. In aqueous solution, gradual hydrolytic
degradation was observed [
321
]. The rapid temperature-triggered irreversible
hydrogel formation, high-mechanical strength, and degradation behavior render
this polymer mixture system suitable for use in injectable biomedical materials
such as a drug delivery depot or a biodegradable scaffold for tissue engineering.
8.3 Biodegradable Shape-Memory Polymers
Shape-memory polymers (SMPs) are a class of smart materials with the ability to
change shape on demand in response to an environmental stimuli [
322
-
325
]. So far,
the most commonly investigated SMPs are temperature-induced SMPs, whose
shape-recovery behavior is triggered by thermal stimuli. Such SMPs have one
shape at certain temperature and are converted to another shape at a different tem-
perature (Fig.
22
). Temperature-responsive SMPs usually require the combination
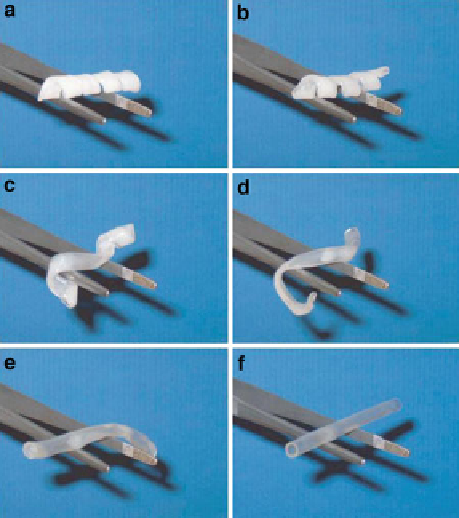
Fig. 22 (a-f) Time series
photographs showing
recovery of shape-memory
tube from start to finish of the
process; total time 10 s, at
50
C. The tube was made of
PCL-dimethacrylate polymer
network that had been
programmed to form a flat
helix. Reprinted from [
323
]
with permission