Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
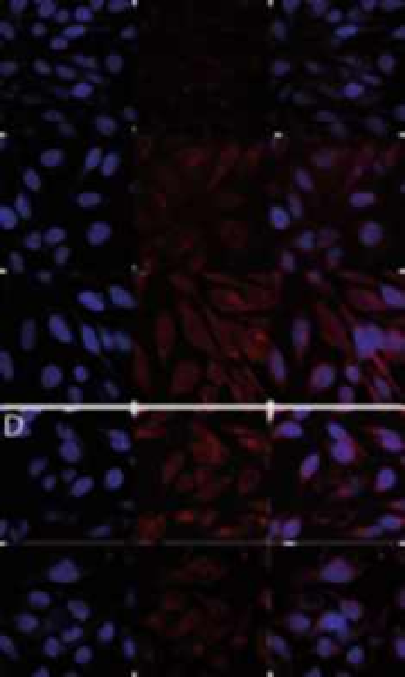
Figure 6.2
Nuclear localization of siRNA depends on the amount of NLS
in the rCPP. HeLa cells were transfected for 1 h with 10 nM
Cy5-labelled siRNA and polymers A-E (N : P 10), fixed and
visualized using confocal laser scanning microscopy. (A)
Polyplex A (100% NLS); (B) polyplex B (75% NLS); (C) polyplex
C (50% NLS); (D) polyplex D (25% NLS); and (E) polyplex
E (0% NLS). Left panels (DAPI stained nuclei, blue), centre
panels (siRNA-Cy5, red), and right panels (overlay). Arrows in B,
C, and D mark nuclear siRNA. The arrow in E marks perinuclear
siRNA.From
J Gene Med
2008; 10: 81-93.
Transcriptional-silencing siRNA targeting an essential promoter
regionoftheelongationfactor1alpha(EF1A)wasusedtoinvestigate
nuclear delivery in HeLa cells. Cytoplasmic EF1A mRNA levels
were quantified by real-time RT-PCR at 48 h post-transfection with
the rCPP series. EF1A levels standardised to GAPDH control showed
a gradual decline with increased NLS content showing a clear
NLS-dependency. Maximal reduction (~60%) was observed for

Search WWH ::

Custom Search