Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Conductive elastomer- or foam-based sensors do, however, suffer from some significant
disadvantages:
•
An elastomer has a long nonlinear time constant. In addition, the time constant of the
elastomer when force is applied is different to the time constant when the applied force
is removed.
•
The force - resistance characteristics of elastomer-based sensors are highly nonlinear,
requiring the use of signal processing algorithms.
•
Due to the cyclic application of forces experienced by a tactile sensor, the resistive
medium within the elastomer migrates over a period of time. Additionally, the elastomer
will become permanently deformed and fatigued, leading to permanent deformation of
the sensor. In the long-term, its stability will become poor, necessitating replacement
after an extended period of use.
Due to the simplicity of design and interfacing of these sensors, even with their electrical
and mechanical disadvantages, the majority of industrial analog touch or tactile sensors
are, nonetheless, based on the principle of resistive sensing.
2.4 Magnetic-Based Sensors
A magneto-resistive or magneto-elastic material is one whose magnetic characteristics
change with an externally applied physical force. Magneto-elastic sensors have a number
of advantages, such as high sensitivity and dynamic range, no measurable mechanical
hysteresis, a linear response, and physical robustness. Of the two approaches to designing
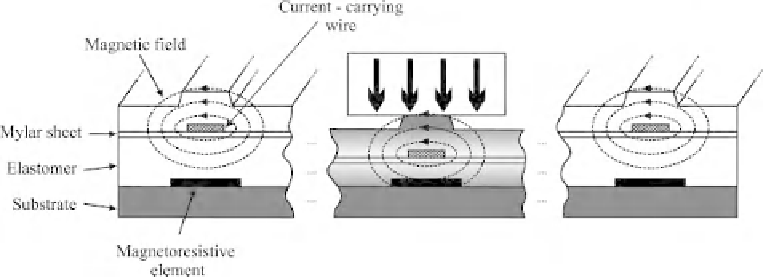
tactile sensors based on magnetic transduction, one is based on the principle that the
movement of a small magnet by an applied force will cause the flux density at the point
of measurement to change (Figure 2.4). The observed change in flux density can then
be measured by using either the Hall effect or a magneto-resistive device. The second
approach involves fabricating the core of a transformer or inductor from a magneto-
elastic material that will deform under pressure and cause the magnetic coupling between
Figure 2.4
Magneto-resistive sensor using current-carrying wires (recreated) [8]