Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Testing Probe
Electrodes
Supports
Beams
5mm
Figure 4.34
The macromachined tactile sensor
to estimate the softness of test objects. In addition, it was also required to employ an
additional quantification technique, rather than the conventional qualitative and heuristic
approach, in which the test objects were labeled in terms very soft, soft, and so on. The
durometer (Shore) softness test is one of the most commonly used hardness/softness tests
for elastomeric materials. The durometer gauge measures the depth of surface penetration
of an indenter of a given geometry. Since both force and deflection are measured, the
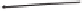
durometer is typically used as a stiffness indicator of which a working concept is shown
in Figure 4.35. When the durometer is pressed against an object, depending upon the
softness, a calibrated spring contained within the indenter tip (whose shape and size can
vary depending upon the type of durometer) is compressed and the softness number can
then be read from a dial connected to the spring. The durometer hardness test is defined
by ASTM D 2240, which covers seven different types of durometers: A, B, C, D, DO,
O, and OO [19].
Table 4.2 summarizes the overall information about the A- and OO-type durometers
that were used in this study. In this group, type OO was used for the measurement of
very soft materials.
Figure 4.35
A picture of the durometer used in this study