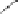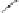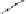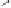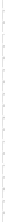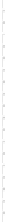Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
Foreman CIF 30 Hz
Foreman QCIF 15 Hz
39
39
MCTF with Open-Loop
MC
T
F
wi
t
h
C
lo
s
ed
-
L
oo
p
T
raditional
GOP with I
B
BP
M
CTF with O
p
en-Loop
M
CT
F
w
it
h
C
lo
s
e
d-
L
oo
p
T
raditional G
O
P with IBBP
38
38
37
37
36
36
35
35
34
34
33
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
kbits/s
kbits/s
(a)
(b)
Bus CIF 30 Hz
Bus QCIF 15 Hz
36
36
MCTF with Open-Loop
MC
T
F
wi
t
h
C
lo
s
ed
-
L
o
op
T
rad
it
ional
GOP
with I
B
BP
M
CT
F
w
it
h
O
p
en
-
L
o
op
M
CTF with C
l
osed-Loop
T
raditional G
O
P with IBBP
35
35
34
34
33
33
32
32
31
31
30
29
30
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
80
90
100
110
120
130
140
150
160
170
180
190
200
210
220
kbits/s
kbits/s
(c)
(d)
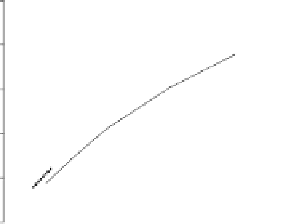
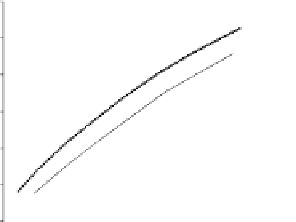
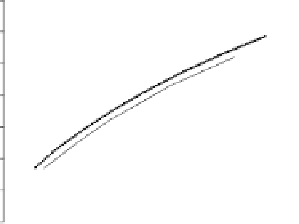
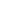
Fig. 3.8.
Comparision of PSNR performance between the GOP structures of MCTF
and IBBP. All schemes are coded with single layer configuration [12].
In summary, from the perspective of prediction e
ciency, MCTF shows
better performance than traditional GOP structure of IBBPBBP. It is
a tool for temporal scalability, and also for coding e
ciency.
3.2.2 Spatial Scalability and Inter-Layer Prediction
The spatial scalability is achieved by the concepts used in MPEG-2, H.263,
or MPEG-4. Sequences of different spatial resolutions are coded in separated
layers. Conceptually, a pyramid of spatial resolutions is provided.
To remove the redundancy among different spatial layers, a large degree
of inter-layer prediction is incorporated. Specifically, the residues and mo-
tion vectors of an enhancement-layer frame are predicted from the those in
the subordinate layers. Fig. 3.9 presents an example of inter-layer prediction
with 2 spatial layers. The spatial base layer is coded with the structure of
hierarchical B pictures and the spatial enhancement-layers are coded by the
MCTF.