Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
and 4 levels for ensuring inter-operability of these applications. The profile
defines the color space, resolution, and scalability of the bitstream. The levels
define the range of frame resolution, luminance sample rate, the number of
video and audio layers supported for scalable profiles, and the maximum bit
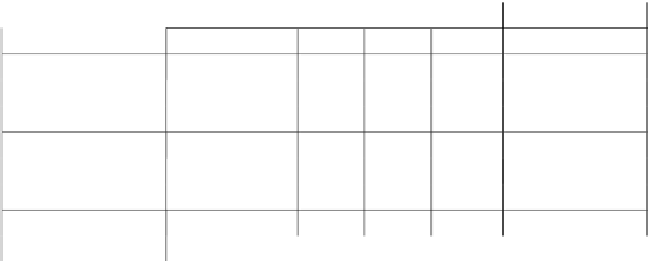
rate per profile. The following table shows the MPEG-2 Profiles and Levels.
Simple
Main
SNR
Spatial
High
Profile
Profile Profile Profile
Profile
no B pictures
spatial or SNR
High Level
1920108030 ≤80
≤100 Mbps
1920115225
High-1440
1440108030 ≤60 ≤60 ≤80 Mbps
1440115225
Main
70448030 ≤15 ≤15 ≤15 ≤20 Mbps
70457625
Low
35224030 ≤15 ≤4 ≤4 ≤20 Mbps
35228825
MPEG-2 Scalability
Scalable video is only available on Main and higher profile. Currently there
are four scalable modes, and these are,
Spatial Scalability: The spatial scalability codes a base layer at lower reso-
lution, and the up-sampled reconstructed base layers are then used as
prediction for the enhancement layers.
Data Partitioning: Data partitioning is a frequency domain method that
breaks the block of 64 DCT quantized transform coe
cients into two
partitions. The first, higher priority partition forms the base layer, which
contains the header information, motion vectors and more critical lower
frequency coe
cients. The lower priority partition is in the enhancement
layer that carries higher frequency AC data.
SNR Scalability: SNR scalability is a spatial domain method where the base
layer uses coarse quantization, and the prediction errors will be further
quantized and VLC coded to form the enhancement layer. The enhance-
ment layer is used to refine the base layer to construct a higher quality
picture.
Temporal Scalability: The base layer codes video at a lower frame rate, and
the intermediate frames can be coded in the enhancement layer using the
base layer information as reference for prediction.