Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
Previous frame
Previous frame
Current frame
Current frame
Future frame
Future frame
MV2
MV2
MV1
MV1
+
+
+
+
forward
prediction
error
forward
prediction
error
backward
prediction
error
backward
prediction
error
previous location
previous location
+
+
+
+
current location
current location
P-frame
output
P-frame
output
future location
future location
Average
Average
MV1
MV1
interpolative
prediction
error
interpolative
prediction
error
1 or 2 MVs
1 or 2 MVs
B-frame
output
B-frame
output
Prediction error
Prediction error
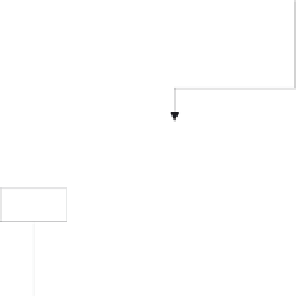
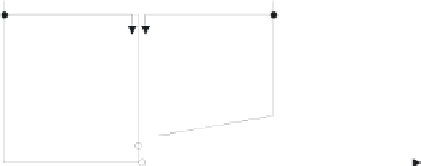
Fig. 2.14.
Forward predictive coding and bi-directional predictive coding.
The advantages of bi-directional prediction are
• B-frames use much less data bits than P-frames.
• B-frames have less noise, which is the result of averaging between previous
and future frames.
• Newly panned or uncovered area can be accurately predicted from the
future reference frame.
2.4 Overview of Video Coding System
There are two main techniques used in all the video coding systems, i.e., the
DCT based Intra frame data compression technique to remove the spatial re-
dundancy in an image frame, as is described in Section 2.2, and the motion
compensated prediction based Inter frame data compression to remove the
temporal redundancy in between successive frames, as is described in Sec-
tion 2.3. In this section we will introduce the architecture of the video coding
system, and the coding and decoding process of various types of pictures.
2.4.1 Video Bitstream Hierarchy
The video coding standard is primarily a specification of bitstream semantics.
The video bitstream is usually arranged in layers, each corresponds to a hi-
erarchy, as is shown in Fig. 2.15. The functions of each of the hierarchy are
very useful as are explained in the following: