Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
This estimate for C
′
ap
will be positive whenever there is a bias between the
number of R and S groups, or when N
R
= N
S
. This bias is influenced by the
size and shape of the group G, the discrimination function f , the amplitude
of the invertible noisy permutation F , and the content of the original image.
The bias increases with the group size and the amplitude of the permutation
F . Smoother and less noisy images lead to a larger bias than images that are
highly textured or noisy.
In a practical application, for some natural images, by defining a different
discrimination function f , choosing the group size, selecting the number of the
pixels that should be flipped, or selecting embedding mask M =[A
1
,,A
n
]
for example, the embedding capacity can be further improved.
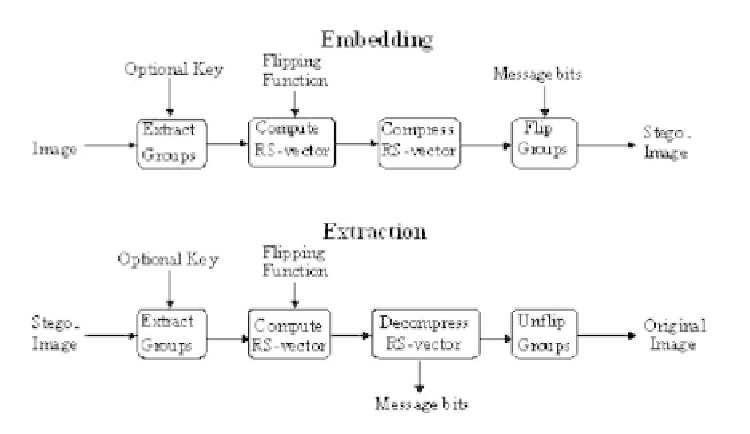
Fig. 13.4.
Diagram for the distortion-free data embedding and extraction algorithm.
The method provides a high embedding capacity while introducing a very
small and invertible distortion. A number of experimental results show that
the highest capacity was obtained for relatively small groups where n is ap-
proximately equal to four.
Lossless G-LSB Data-Embedding Method
Celik et al. [8] presented a high capacity, low distortion reversible data hiding
technique. A generalization of the least significant bit (GLSB) modification is
proposed as the data-embedding method. Lossless recovery of the host signal
is achieved by compressing the lowest levels instead of the bit planes of the
signal. The levels chosen were those susceptible to embedding distortion and