Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
coding. Fig. 2.1 summaries the data compression techniques that are com-
monly used today. Working independently, none of these data compression
techniques can provide significant data compression. However, using the right
combination of several techniques, very e
cient data compression systems can
be made. Several such combinations have been adopted as international stan-
dards. The JPEG/JPEG2000 is used for image coding. H.26x, and MPEG are
used for video coding.
Image/video compression
Lossless coding
Lossy coding
Huffman
coding
Predictive
coding
Frequency
domain
Hybrid
coding
Importance
Arithmetic
coding
JPEG
DPCM
Transform
Filtering
Run length
coding
MPEG
DM
Sub-band
Subsampling
H.26x
LZW coding
Motion
estimation
Quantization
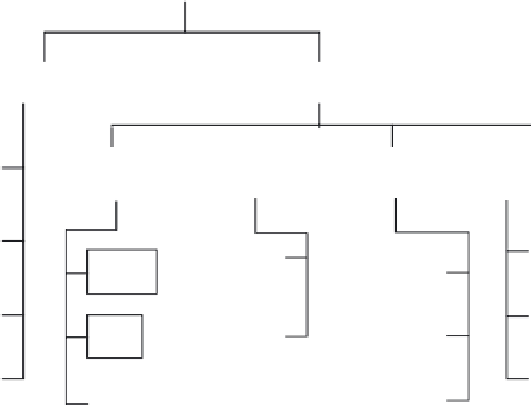
Fig. 2.1.
Various image/video coding techniques.
Fig. 2.1 shows the classifications of various image and video coding tech-
niques. If the compression scheme does not cause any information loss, but
only reduces the number of bits required to describe the data, it is called
Lossless Coding. Lossless Coding is a reversible process. If alternatively, in
order to achieve higher compression ratio, it is permissible to have some small
distortions or information loss. The scheme is called lossy coding. This is irre-
versible. In this chapter, the common image/video coding schemes are intro-
duced. These are used for state of art image and video coding standards. Other
techniques that are di
cult to implement are not described. Examples of such
schemes are known as Karhunen-Loeve Transform (KLT), Walsh-Hadamard
Transform (WHT), vector quantization, and fractal transform for example.
Details of the mathematics of those techniques are omitted. The principles of
using them for data compression using these techniques are explained.