Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
if the number of m
i
y
(f,r)
variance σ
2
N
R
s, FR
is large enough.
i
That is,
N (µ, σ
2
),
if b =1;
c∼
(7.13)
N (−µ, σ
2
),
if b =0.
In the case of detection from original frames, c follows c∼N (0,σ
2
).
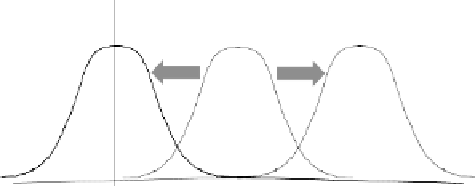
The transition of the normal distribution due to WM embedding
is shown in Fig. 7.8: the normal distribution of the original frames
N (0,σ
2
) is shifted to either N (µ, σ
2
)orN (−µ, σ
2
) according to
embedded bit b.
Step D5: Determine the embedded bit b by comparing c with a threshold
value T (> 0):
Watermarked frames
,
Original frames,
Watermarked frames
,
2
b
=
)
N
(,
σ
2
)
N
(0,
σ
)
b
=
)
N
σ
2
(, )
0
Fig. 7.8.
Transition of distribution in WM embedding.
⎧
⎨
1,
if c≥T ;
b =
0,
if c≤−T ;
(7.14)
⎩
not detected,
if−T<c<T.
Multiple-bit-WM Scheme
WM embedding
Each region y
(f,r)
is divided into K subregions y
(f,r,k)
s(k =1,,K)and
the 1-bit embedding scheme is then applied to each subregion:
Step E1: Do the following steps over f =1, 2,.
Step E2: Input the original frame y
(f )
and divide y
(f )
into RK subregions
y
(f,r,k)
s(r =1,,R,k =1,,K) consisting of the correspond-
ing pixels: y
(f,r)
k
y
(f,r)
k,i
N
(RK)
, which satisfies y
(f )
=
1≤i≤
=
r=r
′
y
(f,r
′
,k)
k=k
′
y
(f,r,k
′
)
r,k
y
(f,r,k)
, y
(f,r,k)
=∅,andy
(f,r,k)
=
∅(See example shown in Fig. 7.9).