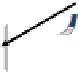Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
picture quality. Resolving the tradeoff between these conflicting requirements
has been one of the main objectives in research on video watermarking. The
video watermarking methods reported so far have trouble doing this because
they simply utilize the techniques developed for still pictures and neglect the
properties of motion pictures.
In this chapter we present two adaptive video watermarking techniques
that utilize the properties of motion pictures. One is Motion-Adaptive Em-
bedding in which watermarks are allocated to picture areas adaptively based
on motion vectors and deformation quantities among adjacent frames. The
other technique is Statistically Adaptive Detection in which the accumulation
of watermarks is controlled to prevent degradation in the watermark signal
by video processing.
Methods of video watermarking can be classified into two types: those
operating in the pixel domain and those operating in the frequency domain.
In this chapter, we focus on the former and describe representative methods
that operate the luminance values.
In Sect. 7.2 we briefly review the concept of video watermarking and give
an overview of the two techniques that utilize the properties of motion pic-
tures. We describe the first, Motion-Adaptive Embedding using motion es-
timation, and discuss its effectiveness in Sect. 7.3. In Sect. 7.4 we describe
Statistically Adaptive Detection using inferential statistics and discuss its
effectiveness.
Broadcasting
Video provider
User
Copyright
Information
User
Encoded
watermarked
v
i
deo
Original
video
Watermark
embedding
MPEG
encoding
Recording
media
Viewers, etc.
Notify video provider
of illegal copying.
Illegal
copy
Copyright
Information
Networ
k
Auditor
Watermark
detecting
MPEG
decoding
Fig. 7.1.
An example of the use of video watermarking.