Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Mesoporous silica MCM-48 in cubic phase is one of the most
appropriate templates because it has bicontinuous pore geometry,
resulting in representative mesoporous carbon CMK-1. The SBA-15
template has hexagonal array of cylindrical pores. However, its
interconnectivity of the silica channel with micropores leads to
preservation of regular carbon structures (CMK-3) even after silica
removal [58]. The synthesis of carbon nanocage is illustrated in Fig.
10.17B. The speciic surface area and speciic pore volume reaches
up to 1600 m
2
g
-1
and 2.1 cm
3
g
-1
, respectively, in the case of carbon
nanocage at the lowest sucrose to silica ratio [58]. Because of
large pore volume of the carbon nanocage, it would show superior
capability in the biomaterials adsorption [57].
Grabinski
et al
. [49] investigated a risk of exposure to the carbon
nanomaterials, included carbon ibers — CF (10
μ
m diameter),
carbon nanoibers — CNF (100 nm diameter), MWCNT (10 nm
diameter), and SWCNT (1 nm diameter). CF and CNF did not
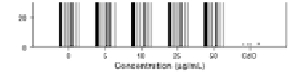
signiicantly affect cell viability (Fig. 10.18). MWCNT and SWCNT
reduced cell viability in a time-dependent manner up to 48 h,
with full recovery of mitochondrial function by the 72 h time point
(Fig. 10.19) [49].
Figure 10.18
Cell viability at 24 and 72 h time points determined via MTT
assay. Cell viability after exposure to CF, CNF, MWCNT, and
SWCNT at four concentrations (5, 10, 25, and 50 lg/mL)
after 24 h (a) and 72 h (b) [49].