Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
the different carbon samples, the bacterial (
S. mutans
) precipitation
eficiency of 30 nm diameter MWCNTs was the highest. SWCNTs were
less effective because they were not easily dispersed before mixing
with the bacteria. The 200 nm-MWCNTs are less effective because
some of them did not precipitate but remained suspended in the
solution. They found that 30 nm-MWCNTs and 200 nm-MWCNTs
are highly adhesive to bacteria (Fig. 10.8). The MWCNTs with 30 nm
diameter had the highest precipitation eficiency, which is attributed
to their adequate dispersibility and aggregation activity.
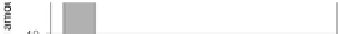
Figure 10.8
Residual amount of
S. mutans
in the supernatant after mixing
with carbon samples at 0.66 mg ml
-1
concentration [3].
iu
et al
. investigated the silver coated carbon nanotubes, against
bacterial attack [40]. The Ag coated CNTs improve the antibacterial
property. The bactericidal rate
K
increases with the thickness of the
Ag ilm (Fig. 10.9). For the same thickness, the bactericidal rate of Ag
coated CNTs is much higher than that of Ag coated pyrolytic carbon.
The carbon nanotubes enlarge the surface area of Ag coating, which
provides high probability for Ag atoms to contact the bacteria leading
to their death [29]. The antibacterial rate against
S. aureus
is lower
than that against
E. coli
[40].
Wang
et al
. [60] used the polycarbosilane as a binder to
consolidate CNTs to the form attractive for implant applications.
The main disadvantage of that bionanocomposite is unsatisfactory
biocompatibility due to the presence of the polycarbosilane [60].