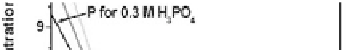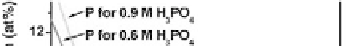Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 9.24
Depth proile of anodic TiO
2
layer formed in electrolytes [47]:
1.5M H
2
SO
4
+ 0.3M H
3
PO
4
, 1.5M H
2
SO
4
+ 0.6M H
3
PO
4
, 1.5M
H
2
SO
4
+ 0.9M H
3
PO
4
. See also Color Insert.
u
et al
. [118] investigated formation of nanostructured TiO
2
thin ilms deposited on silicon, and silicon carbide substrates by
DC magnetic sputtering, with subsequent anodization in acidic
0.1-2.0 wt% HF, and neutral electrolytes containing 1M (NH
4
)
2
SO
4
and 0.5 wt% NH
4
F. They described the effect of the electrolytes
and substrates on the microstructure of the anodized thin ilms.
Nanoporous ilms (Fig. 9.25) formed on silicon substrates with an
average pore diameter of 25 nm and interpore distance of 40 nm
was obtained [118]. Yu
et al
. showed the possibility of the formation
of anodic ilm on silicon carbide substrate, too [118]. They did the
anodization in 0.3 wt% HF electrolyte at 2.5 V. The obtained ilm
was composed of the individual clusters that exhibited a laminated
structure (Fig. 9.26). The unique microstructure is related with
different orientation of the titanium ilm deposited on silicon carbide
substrate.
Figure 9.25
SEM images of nanoporous TiO
2
thin ilm on silicon substrate
formed in 0.5% HF electrolyte at 3 V; high (a) and low (b)
magniications [118].