Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
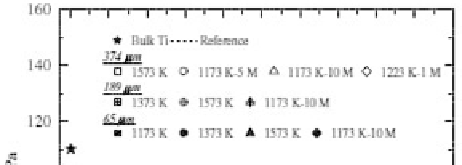
Porous Ti compacts, made by powder metallurgical process,
have porosities ranging from 5.0 to 37.1 vol% [65]. In these porous
Ti compacts, the rough surface depends on Ti initial powder size, so
the porosities and mechanical properties of porous Ti compacts can
be controlled by changing powders size and sintering conditions. Oh
et al
. found that Young's modulus and bending strength of porous Ti
compacts having the porosity approximately 30 vol% are close to
those of human cortical bone [65]. Increasing porosity results in a
signiicant decrease in Young's modulus (Fig. 9.1).
Figure 9.1
Young's modulus of sintered porous Ti compacts as a function
of porosity. Porous Ti compacts sintered with applied pressure
are abbreviated as temperature (K)-pressure (M) [65].
The Ti metal in all cases during processing (sintering, heat
treatment, and etching) in the oxygen-containing atmosphere
spontaneously forms a protective TiO
2
layer. When the Ti implant is
inserted into the human body, the surrounding tissues directly contact
the TiO
2
layer on the implant surface. The surface characteristics
of the TiO
2
layer determine the biocompatibility of the Ti implant
[112] and it is important to increase the biocompatibility of the