Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 5.
Impact morphology of viscoplastic drops (equilibrium diameter:
∼
2.5 mm), on a parafilm
substrate from a fall height of 50 mm [16].
small diameter [23], however for high yield stress magnitudes and low impact ve-
locities drops still preserve the original form they have after detachment from the
capillary.
Another interesting feature of viscoplastic drop impacts is the linear dependence
of the maximum spreading diameter on the yield stress magnitude, displayed in
Fig. 6, whereas in Newtonian drops the same quantity depends on viscosity ac-
cording to a power law [6, 17, 24]. Similar to shear-thinning fluids, the influence
of surface wettability on viscoplastic drop impacts is only noticeable after the end
of the inertial expansion stage, as shown in Fig. 7, which compares drop diame-
ters of viscoplastic drops impacting respectively on a hydrophobic Parafilm surface
(equilibrium contact angle:
105
◦
) and a hydrophilic glass surface, for different
Weber numbers. In the viscoplastic regime (
ˆ
B>
1), drops exhibit only small retrac-
≈




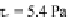



















































































































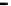
Search WWH ::

Custom Search