Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 2.
Dimensionless drop diameter,
β
, plotted against time for shear-thinning drops (
K
=
5
.
064 Pas
n
,
n
=
0
.
084) impacting on glass and parafilm-M surfaces [16].
Figure 3.
Maximum spreading diameter of shear-thinning drops impacting on substrates of different
wettability (glass and parafilm) [16].
is barely noticeable for impacts on the glass surface, where the slow capillary driven
spreading continues directly after the fast spreading of the inertial expansion phase.
In particular, the maximum spreading diameter, reported with respect to the We-
ber number in Fig. 3, can be considered the same for the two surfaces, within
experimental error.
Increasing the mass fraction of Xanthan gum increases the consistency coeffi-
cient
K
, however it also decreases the power law index
n
. In other words, fluids
become thicker but at the same more shear-thinning. Again, fluids exhibiting large
degrees of shear-thinning (i.e., with a value of the power-law exponent close to














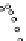









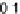



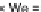

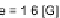
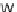






































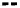













Search WWH ::

Custom Search