Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 3.
Zeta potential
vs.
pH (in aqueous 1 mM KCl) for PTFE (data from Werner
et al.
[65]) and
Teflon AF1600 (data from Zimmermann
et al.
[61]). Reprinted with permission from Paneru
et al.
[51]. Copyright 2011 VSP.
Figure 4.
Critical surface tension of wetting,
γ
C
, for Teflon AF with various ratio between the PDD
and TFE monomers. Reprinted with permission from Quinn
et al.
[18]. Copyright 2003 American
Chemical Society.
proximity of the polymer surface. However, it does not affect the wettability of the
Teflon AF1600 surface which is very hydrophobic. The critical surface tension of
wetting,
γ
C
, obtained with alkanes using the Zisman approach [15, 64] for several
amorphous fluoropolymers (Teflon AF) with different PDD:TFE ratios is shown in
Fig. 4.
The PDD:TFE ratio has a minor effect on the critical surface tension of wetting.
All values for amorphous fluoropolymers are intermediate between those obtained
on -(CF
2
-CF
2
)
n
- (i.e., PTFE) and on a monolayer of closely packed -CF
3
groups.
Therefore the hydrophobicity of Teflon AF is due to the predominant exposure of




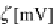
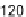

































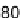

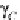
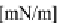


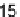








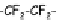










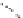
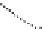





























































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search