Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
first agitating the partially
dodecyl-substituted alginate derivative (alginate substituted with low amounts of dodecyl
chains) under mechanical stress, creating a shear thinning water solution without NaCl;
then repeating this in the presence of NaCl, resulting in physical gelation and particle
formation via hydrophobic interactions; and
Consequently Leonard et al. used a three-stage process:
finally adding small amounts of CaCl
2
to
improve the mechanical properties of the beads. The average size (10
100 μm) and
distribution of the resulting particles depended on the hydrophobic character of the solution
and on dispersion conditions, but because of the absence of NaCl in the initial stages, this
procedure can be used for the mild entrapment of biological substances such as proteins.
-
11.3.3
Nanoparticles for protein delivery: production, assembly and structure
New approaches for water-based drug delivery vehicles, and strategies to optimize
nanoparticle properties such as size, charge and hydrophilicity, are receiving increasing
attention. Prokop et al.(
2001
) have proposed a novel production method for nano-
particles of multi-component polymeric complexes that are candidates as delivery
vehicles for biological molecules such as proteins and drugs. Using either batch or
continuous processing, and in the absence of organic solvents, stable nanoparticles that
are insoluble in water or buffered media are produced using biocompatible and/or natural
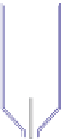
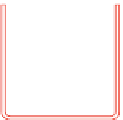
polymers. In the batch system an anionic polymer solution is introduced into a syringe
and slowly extruded (by means of controlled air pressure) through a needle and into an
ultrasonic nebulizer. A
fine mist of anionic solution forms at the probe tip and falls into a
cationic solution placed in an agitated receiving bath (
Figure 11.12
). Nanoparticles are
produced
'
instantly
'
on contact of the extruded liquid with the receiving bath. The
Regulated gas
pressure inlet
O-ring
Syringe
Anionic solution
Glass syringe
Needle
Ultrasonic
transducer
Nozzle
Anionic solution
vapour
Cationic
solution
Figure 11.12
Batch production of nanoparticles of multi-component polymeric complexes. Adapted from
Prokop et al.(
2001
) with permission from John Wiley & Sons.




































Search WWH ::

Custom Search