Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
interactions. Hydrogen bonds occur, for example, with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG).
Hydrophobic interactions are responsible for the formation of a network when alkyl
chains are grafted to chitosan by an acid or an aldehyde. Moreover, these interactions can
arise from intrinsic properties of the graft. For instance, functionalization with Pluronics
(
Chapter 6
) allows the formation of thermally gelling systems due to graft dehydration,
leading to increased inter-chain association. Grafting with NIPAm (
Chapter 4
) allows the
formation of a temperature-sensitive system.
As swelling depends on the electrostatic repulsion of the free ammonium groups, it
only occurs in acidic conditions, which limits its potential applications. Grafted chitosan
presents interesting properties, for example, in wound-healing, where biocompatible
chitosan derivatives can exhibit enhanced bacteriostatic activity. Grafting of hydrophobic
groups onto chitosan also allows the incorporation of lipophilic drugs. That said, such
grafted chitosan gels do not have signi
cant advantages over covalently cross-linked
gels, since they may require the use of potentially toxic auxiliary molecules for their
preparation, and this preparation is usually more dif
cult.
11.3.1.3
Chitosan
-
PVA complexes
Chitosan
culty than PECs, but not as
easily as ionically cross-linked gels. They do not exhibit pH-sensitive swelling, and PVA
does not have any speci
-
PVA complexes can be prepared with less dif
cally exploitable properties, as do some polyelectrolytes.
Therefore, chitosan
field of application.
However, as the use of PVA in medical and pharmaceutical applications is well docu-
mented, chitosan
-
PVA complexes have a relatively narrow
PVA complexes represent an interesting alternative to PEC and
ionically cross-linked gels for the preparation of biocompatible drug delivery systems,
if a pH-controlled drug delivery is not required. Like chitosan, PVA is non-toxic,
biodegradable and highly biocompatible.
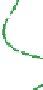
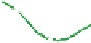
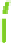
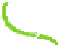
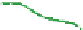
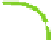
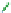
The structure of chitosan
-
PVA hydrogels (
Figure 11.8
) can be considered as inter-
mediate between PEC hydrogels and networks formed by grafted chitosan, discussed in
-
(a)
(b)
H
Hydrogen bond
Crystalline junction
Figure 11.8
Proposed structure of chitosan
-
PVA hydrogel (
-
chitosan;
▬
PVA): (a) prepared by autoclaving
method; (b) prepared by freeze/thaw method, showing hydrogen bonds and crystalline junctions.
Adapted with permission from Berger et al.(
2004a
) © 2004 Elsevier.





















































































































































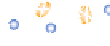


































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search