Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Laser
beam
Hydrogel
Silicon
Laser
beam
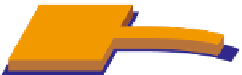
Schematic view of the MEMS sensor platform based on a microcantilever patterned with
environmentally responsive hydrogel: at rest (top) and after bending by swelling (bottom). Adapted
with permission from Hilt et al.(
2003
) © 2003 Springer.
Figure 11.6
within the interphase and (iii) their condensation and contraction on to the neutralized gel.
This sequence could be repeated up to 20 times, to give a macroscopic gel of a few cubic
centimetres with an onion-like structure composed of independent gel membranes.
11.1.5
Hydrogels as ultra-sensitive sensors
Another active research area is the development of micro-electromechanical systems
(MEMS) based on the ultra-sensitivity of microcantilevers and the various responsive
abilities of environmentally sensitive hydrogels. For example, pH-sensitive hydrogels
can be laid down in a precise pattern on microcantilevers to create an ultra-sensitive pH
microsensor, as shown schematically in
Figure 11.6
(Hilt et al.,
2003
). The chemically
cross-linked hydrogel
film is capable of sensing a change in environmental pH and
equilibrates within a few minutes. Photolithography is used to pattern the polymer
networks
for example of poly(methacrylic acid) (PMMA), produced by reacting
methacrylic acid monomer with poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate (UV free radical
copolymerization)
-
and adhesion is generated between the silicon substrate and the
polymer using an organosilane coupling agent.
In the anionic network of the hydrogel, ionization of the acid groups occurs when the
pH is raised above the pK
a
. With deprotonation of the acid groups, electrostatic repulsion
between chains increases the hydrophilicity of the network, so water is absorbed.
Swelling of the hydrogel induces a de
-
ection of the cantilever. The dynamic and
equilibrium de
ection characteristics of such microcantilevers were examined in buf-
fered solutions of various pH.
An example of data from such a sensor is shown in
Figure 11.7
. Avalue of 20 μm per
pH unit was found for the highest sensitivity sample, which gives a resolution for optical-
based laser detection set-ups of 1 nm de
pH= 5×10
-
5
. It is to be expected that
the swelling properties of the polymer hydrogels, and therefore the sensitivity of such
devices, can be tailored by changing the amount of cross-linking, by increasing the
porosity of the network or by varying the polymer
ection for
Δ
film thickness.












Search WWH ::

Custom Search