Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
5
4
3
2
1
0
−
1
−
2
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
T
(°C)
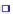
Storage (
●
) and loss (
○
) moduli of stereo-complexes of PMMA in o-xylene at c = 12.6 wt%. From
Pyrlik and Rehage (
1975
).
Figure 8.13
20
10
0
10
−
1
10
0
10
1
Time (s)
10
2
10
3
10
4
Stress relaxation modulus measured at a fixed strain (0.5%) versus time for s-PMMA
-
toluene gel
with c = 10 wt%. From Berghmans et al.(
1994
) © 1994 American Chemical Society.
Figure 8.14
8.4.2
The two-step mechanism in
s
-PMMA solutions
IR, DSC and rheological experiments performed on progressive cooling of solutions of
s-PMMA point towards a two-step mechanism: a very fast intermolecular conformational
change, followed by a further intermolecular association. Gels formed at a measurable rate
(e.g. cooled to an intermediate temperature of, say, 46°C, annealed for a time and then cooled
again at 40°C) show measurable time-dependence effects related to the progressive associ-
ation of the primary structure (single helix) into more aggregated structures. Annealing also
has an important effect on the value of the enthalpy change on melting and re
ects the
contribution of intermolecular associations. Berghmans et al.(
1994
) illustrated the two-step
mechanism for gelation of s-PMMA in toluene, as shown in
Figure 8.15
.
In studies of the self-complexation of s-PMMA, Berghmans et al.(
1994
) found
no
firm evidence for the formation of a double helix at the very beginning of the










































Search WWH ::

Custom Search