Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
T
(ºC)
Sol
150
A
10 0
Gel I
50
B
0
Gel II
-50
Gel II.DEM crystals
0
10
20
30
10
2
×
c
(g
cm
-3
)
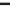
Temperature
-
concentration phase diagram of HTPVC in dimethylmalonate gels aged for 24 h at
20°C: differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) experiments at 20°C min
‒
1
(
●
); ball-drop method at
2°C min
‒
1
(
□
). Adapted with permission from Mutin and Guenet (
1989
) © 2002 American
Chemical Society.
Figure 8.1
different PVC chains, and where the interaction has an electrostatic origin. As a con-
sequence, gel elasticity should be enhanced by the polymer
solvent complex.
Although several authors agreed with this general picture, there are a number of points
which are still unclear. First of all, DSC showed no clear endotherm (melting peak) when
the HTPVC gels were heated, either in diethylmalonate or other solvents in well-
controlled conditions, at
-
150°C, around the melting temperature
expected for the crystalline component. Depending on sample preparation, the thermo-
grams observed by Mutin and Guenet were quite different. (i) The thermogram of a
freshly prepared gel always contained one endotherm, corresponding to gel melting as
measured independently by the ball-drop method (data shown in
Figure 8.1
). This
temperature was independent of the solvent, but extrapolation of the melting area of
the peaks at zero heating rates gave a zero melting enthalpy! (ii) Reheating a gel that had
been molten and cooled to 20°C in the DSC pan showed no endotherm. Further, this
endotherm did not reappear, even after several days of ageing at room temperature. In
addition, no formation exotherm could be detected, unlike with other gelling systems. In
Figure 8.1
the thermal limits of existence of Gel I were con
the limit of 100
-
rmed by the ball-drop
method, the method detecting the softening of the elastic gel above 100°C. However, the
crystalline fraction was dif
cult to quantify. WAXD diffraction measurements by Hong
and Chen (
1998
) on PVC with a syndiotactic content of 0.30 to 0.35 gelled in bromo-
benzene (BrBz) and dioxane (DOA) showed only amorphous peaks, indicating that the
size of the microcrystals was too small to produce a crystalline diffraction pattern in the
X-ray intensity curves. However, the peak of amorphous scattering in PVC
-
DOA gel
was much sharper than that in PVC
-
BrBz gel, implying that PVC
-
DOA gel has a thicker






















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search