Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 7.1 Imino acid composition and denaturation temperatures of collagens from various sources.
Imino acid (wt%)
Cod
Ling
Portuguese dogsh
Megrim
Tuna
Calf skin
Pro
10.3
10.9
11.2
12.8
12.4
13
Hyp
7.1
6.9
7.5
9.1
9.2
12.2
Pro +Hyp
17.4
17.8
18.7
21.9
21.6
25.2
T
m
(°C)
15
19.5
20.9
27.9
28.8
36
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
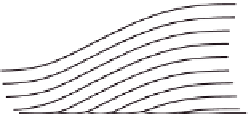
Structure of collagen fibres: (a) fibres are bundles of twisted fibrils; (b) fibrils are made of
rods arranged in parallel and staggered arrays (periodic spacing 64 nm); (c) each rod is a
right-handed triple helix; (d) the single collagen strand is a left-handed helix.
Figure 7.1
supramolecular arrangement of the collagen rods in
fibrils is called the quaternary
structure. The
fibres are strengthened by covalent bonds and thus are insoluble. The
hierarchical arrangement of collagen in the native state is shown in
Figure 7.1
. At larger
scales, in tissues, the assemblies of
fibres form a wide variety of patterns.
7.2.3
Amino acid composition in collagens from various sources: mammalian and fish
Mammalian collagens are the most common, but other sources have been exploited,
including those from piscine sources, particularly skins. The main difference between
mammalian and
fish collagens lies in their imino acid composition (
Table 7.1
). In
contrast to mammalian collagens, the content of these particular imino acids in
sh
collagens varies signi
cantly in the range 17
-
22 wt%, while in mammalian collagens it
is close to 25 wt%.
Fish are non-homoeothermic, and it was recognized that the denaturation temperatures
of the various collagens parallel the natural environment temperatures of the species from


































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search