Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
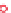
1000
100
10
1
0.1
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
End-cap length (carbon unit)
Effect of end-cap length on the Newtonian viscosity of an aqueous solution, c = 2% w/v of HEUR
(M
w
= 3.5 × 10
4
g mol
−
1
) at room temperature. Reproduced from Annable et al.(
1993
) with
permission of the American Institute of Physics for The Society of Rheology.
Figure 6.7
6.3.5
Triblock copolymers with a hydrophobe core
Poly(ethylene oxide)
n
-poly(propylene oxide)
m
-poly(ethylene oxide)
n
(PEO
n
-
PEO
n
)
triblocks, available commercially as Pluronic® (also called poloxamers), are non-ionic
macromolecular surface-active agents. They are an important class of surfactants
(Alexandridis and Hatton,
1995
) with widespread industrial applications not only in
detergents, emulsi
PPO
m
-
cation, lubrication, cosmetics and inks, but also in pharmaceutical
applications for drug solubilization and controlled release.
The PEO
n
-
PEO
n
block copolymers are available in a range of molecular
masses and PPO/PEO ratios. The mass of the PPO group can vary between 950 and
4000 g mol
−
1
, the PPO/PEO percentage varies between 10% and 80% and water
solubility increases with PEO content. The cloud point, the temperature at the
beginning of phase separation, for a polymer concentration of 1%, varies between
10°C and 100°C from low to high PEO content. Besides surface activity, these
copolymers have a
PPO
m
-
(viscosity or minimum concentration required
to obtain a gel at room temperature) which increases when the PPO block molecular
mass increases and the PPO/PEO ratio decreases. In practice, the rheology of con-
centrated solutions needs to be carefully examined (see the next section). Micelle
formation is observed with increasing temperature, and is associated with an endo-
thermic enthalpy change.
'
thickening power
'
6.4
Rheology of associating polymers
As already explained in
Chapter 4
, associating polymers have non-permanent (labile)
junctions, giving rise to some interesting solution rheology. At low shear rates, the
solutions exhibit liquid-like behaviour with a Newtonian plateau, but the main interest
in applications of associating HM water-soluble polymers is the very important increase
of the zero-shear viscosity compared to that of the unmodi
ed polymer.



























Search WWH ::

Custom Search