Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
10.2
Cultured Cell-Derived ECM Porous Scaffolds
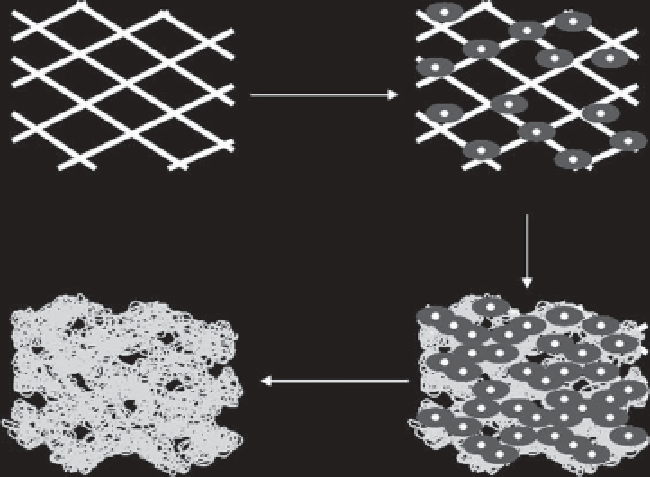
Preparation method of ECM scaffolds by three-dimensional culture of
cells in a selectively removable template is shown in Figure 10.1. Cells are
cultured in the template. ECM is secreted by cells and deposited on the
template. After cell culture, cellular components are removed by decel-
lularization methods. The template is selectively removed from the ECM.
ECM porous scaffolds are obtained after decellularization and template
removal.
The method has been used to prepare ECM porous scaffolds by cul-
turing human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs),
human dermal fi broblasts and human articular chondrocytes [29]. PLGA
knitted mesh is used as a template. MSCs, fi broblasts and chondrocytes
are seeded and cultured in the template. The cells adhere, proliferate
and secrete ECM in the template. After culture for 5 to 6 days, the cel-
lular components are removed by the decellularization method of freeze-
thaw cycling plus the treatment with ammonium hydroxide. The PLGA
mesh template is selectively removed by the treatment of immersion in
0.5 M Na
3
PO
4
aqueous solution at 37
C for 48 hours. The ECM scaffolds
prepared from MSCs, fi broblasts and chondrocytes are referred to as
ECM-M, ECM-F and ECM-C, respectively.
The ECM scaffolds have a mesh-like appearance similar to that of
the PLGA knitted mesh template. Observation by scanning electron
°
Cell seeding
Template
Template/cells complex
Cell proliferation
ECM secretion
Decellularization
Template removal
ECM scaffold
Template/cells/ECM complex
Figure 10.1
Preparation procedure of ECM scaffold from cultured cells.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search