Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
9.2.2
Pickering Emulsion Stabilized with Nanosized
HAp Particles
There has already been active research in Pickering emulsions stabilized
with various functional particulate emulsifi ers: inorganic fi ne particles
such as silica [29, 30], metals [31], and clays [32, 33], organic fi ne particles
such as polymer particles [34-40], microgels [41-45], and shell crosslinked
micelles [46], and more recently, bionanoparticles [47-49]. We have con-
ducted a series of studies on stabilization of emulsion using nanosized
HAp particles as a particulate emulsifi er [50]. It has been confi rmed that
both poorly-crystallized HAp nanoparticles prepared by a wet chemi-
cal method at room temperature [50-56] and highly-crystallized HAp
nanocrystals prepared by calcinations of the HAp nanoparticles at 800
C
[57-61] worked as effective particulate emulsifi ers under specifi c condi-
tions as follows.
When an aqueous dispersion of HAp nanoparticles (or nanocrys-
tals) was homogenized with oil [namely,
n
-hexane,
n
-dodecane, methyl
myristate, methyl trimethyl acetate, chloroform, toluene, 1-undecanol, or
dichloromethane (CH
2
Cl
2
)] in an equal volume ratio, a stable O/W emul-
sion was formed only in the methyl myristate or methyl trimethyl acetate
system. With the other oils, emulsions were unstable and macro-phase
separation into an oil phase and a water phase occurred (Figure 9.2).
These results indicate that only oils having an ester group can form sta-
ble emulsions. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) studies
confi rmed that there is an interaction between the ester group in methyl
myristate or methyl trimethyl acetate molecule and the calcium ion on
the HAp surface. It is considered that HAp show moderate wettability to
the oil phase through such an interaction; as a result, nanosized HAp par-
ticles can be adsorbed to the oil/water interface, leading to stabilization
°
Oils having ester group
Oils having no ester group
Water
HAp nanoparticle
Oil
(Methyl myristate)
Oil (CH
2
Cl
2
)
Water
HAp nanoparticle-stabilized
emulsion
(Pickering emulsion)
Macro-phase
separation
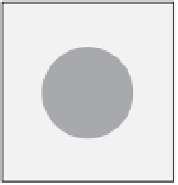
Figure 9.2
Pickering emulsion stabilized using HAp nanoparticles as a
particulate emulsifi er. Stable emulsions are formed using oils having ester group,
and macro-phase separations occur using oils having no ester group.




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search