Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
exists in prokaryotic cells like in eukaryotic cells [23]. Characteristically,
procaryotic cells consist of three main regions, a) fl agella and pili (made
up of surface proteins); b) cell wall and plasma membrane; and c) cyto-
plasm [24]. A typical structure of bacteria is shown in Figure 7.3 [25].
Flagella are found on the bacterial cell surface and consist of fi lamen-
tous protein, and such fl agellum is attached to rotating motor apparatus
connected to the plasma membrane [24]. Bacteria swim in the fl uid with
the movement of fl agella motorized through chemiosmotic potential [26].
Pili are composed of proteins and are very thin and shorter in length
compared to fl agella, so they appear like hairs on the cell surfaces. The
key role of these pili (fi mbriae) is to help in adhesion on the substrate
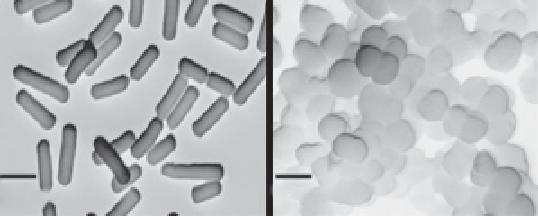
surfaces [27]. On the basis of cell shape, bacteria are grouped in almost
three categories: rod (
bacillus
), sphere (
coccus
), or spiral (
spirilla
and
spiro-
chetes
), although rod shaped bacteria, which are curved, are called
vibrios
(Figure 7.4) [24].
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Cytoplasm
Pilli
Capsule
Plasmid
Ribosomes
Nucleotide
Flagellum
Figure 7.3
A typical structure of prokariotic cell (adapted from ref. [25]).
(
a
)
(
b
)
2
μ
m
2
μ
m
Figure 7.4
The morphology of different types of bacteria: (a)
Escherichia coli
(unpublished image), (b)
S. aureus
(unpublished image).

Search WWH ::

Custom Search