Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Ca
2
+
]
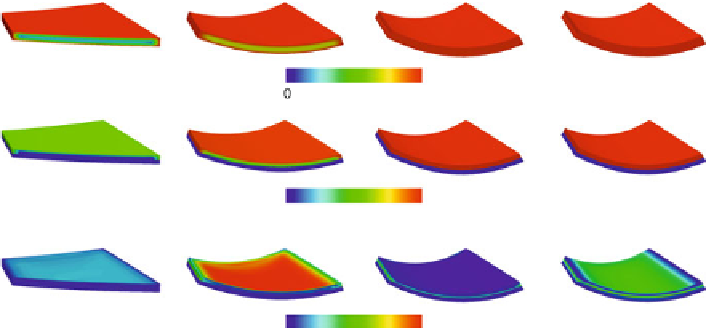
Fig. 5.4
n
D
)
,and
σ
vM
during SM contraction. For the
sake of clarity the deformed strip has been cut virtually, so that the distribution of the appropriate
variables can be identified
Progress of the main variables
[
,
(n
C
+
5.4 Conclusion
In this work, a monolithic coupled two field approach for the chemomechanical pre-
diction of smooth muscle contraction has been developed and implemented into the
framework of the finite element method. The strain-energy function of the mechani-
cal model consists of three parts associated with the constituents inside a SM tissue.
The chemical part has been represented using the four state model by Hai and Mur-
phy (
1988
) triggered by the
dynamic
state of the calcium concentration inside the
muscle.
It has been shown that the model shows an excellent agreement with experimen-
tal data. As the model is implemented into the finite element method it is possible
to study the deformation behavior of SM contraction in a three-dimensional way.
In doing so, deactivated tissue strips have been virtually loaded by an external cal-
cium concentration, leading to a diffusion of the calcium trough the strip. As two
layers, the media and the adventitia, have been considered the strip's deformation is
dominated by a bending mode what seems to be a reasonable result.
We conclude by noting that such class of models in combination with the realis-
tic three-dimensional SM geometries may provide significant contributions for the
understanding, identification and treatment of SM activation.
References
Arner A (1982) Mechanical characteristics of chemically skinned guinea-pig taenia coli. Pflügers
Arch 395:277-284