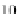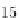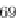Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 26.6
Uniaxial high
strain membrane tangent
modulus
m
E
2
for bovine and
human samples
and FE based analysis of the inflation data enabled determining constitutive model
equations for the long term response of liver capsule. As shown in Fig.
26.7
, both
types of loading, uniaxial and equibiaxial stress, can only be reproduced simulta-
neously by a 2nd order polynomial form of the strain energy potential in the strain
invariant
I
2
.
Based on average biaxial data, a calibrated and physiologically representative
constitutive model was determined in order to include the capsule as an individ-
ual structure in computer simulations, Sect.
26.2.1.1
. To this end, the elastic and
isotropic part of Rubin-Bodner model (Rubin and Bodner,
2002
) was considered
for describing the equibiaxial characteristic of bovine liver capsule. The reference
configuration in the inflation experiment however is different from the
in vivo
ref-
erence state, i.e. before performing the aspiration experiment. In fact, the capsule is
subjected to internal pressure. The intra-hepatic blood pressure averages up to about
50-60 mmHg, i.e. 6.7-8.0 kPa. Assuming that the parenchyma is non-load-bearing
and the liver has a characteristic diameter of 17.5 cm, a guess for the physiological
true tension in the liver capsule at equilibrium yields 0.64 N/mm. The associated
biaxial strain is about 7 %. By means of the multiplicative nature of the stretch, the
'typical' equibiaxial tension-strain characteristic was shifted to this point and the
Rubin-Bodner model calibrated with respect to this new reference curve. To adjust
the model for the human capsule, the finding that the human capsule is about three
times thinner and softer than the bovine capsule was implied, i.e. they 'scale' with
a factor of 3, and thus the Rubin-Bodner parameter
μ
0
was corrected accordingly,
see Table
26.1
.
26.3.2 Finite Element Analysis of the Aspiration Experiment
The FE-model introduced in Sect.
26.2.1.1
was used to analyze the determina-
tion of constitutive model parameters of liver capsule and parenchyma from the
inverse analysis of aspiration measurements. The Rubin-Bodner formulation was