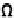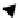Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
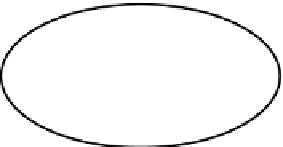
Fig. 23.1
Schematic
representation of the body
Ω
:
the two parts are
Ω
+
and
Ω
−
, separated by crack
Γ
d
.
A traction force holds on
Γ
t
and fluid supply at
Γ
f
Biot's model if osmotic effects are neglected. This model is implemented with the
cohesive segment model by Remmers et al. (
2003
) and de Borst et al. (
2006
)forthe
solid phase assuming quasi-brittle crack growth. Two cases are considered:
•
A pressure discontinuity is introduced similarly to the displacement discontinu-
ity. The flow across the crack surface is evaluated from Darcy's law where the
pressure gradient follows from Terzaghi's one-dimensional consolidation.
•
A continuous pressure enrichment is introduced which resolves the pressure gra-
dient in the vicinity of the crack.
23.2 Governing Equations
The governing equations consist of equations for the bulk and for the discontinuity.
Figure
23.1
shows a body
Ω
with external boundary
Γ
with a traction force on
Γ
t
and fluid supply on
Γ
f
, with
n
the normal unit vector on the boundary
Γ
directed
outwards. The body is cut by a discontinuity
Γ
d
in two domains,
Ω
+
and
Ω
−
.The
normal of the discontinuity
n
+
is directed towards
Ω
+
.
23.2.1 Bulk Behavior
Osmoelastic media have large negatively charged groups fixed to the solid ma-
trix. Counter charges are present in the fluid for electro-neutrality. Due to the fixed
charges the total ion concentration inside the medium is higher than in the surround-
ing fluid. This leads to an osmotic pressure difference and therefore swelling of the
medium. Lanir (
1987
) assumes in osmoelasticity that free ions are always in equi-
librium with the external salt concentration. Ion contribution is therefore neglected
and the medium is described by two constituents only: the solid (s) and the fluid
(f). The constituents are assumed to be incompressible. The material is assumed
linear elastic, isothermal, isotropic, homogeneous and fully saturated. The presence
of the fixed charge causes a deformation dependent pressure difference between the
sample and surrounding fluid. Van't Hoff relation defines the osmotic pressure in