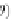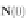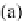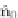Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 12.1
Methodology to remove sidewall IA and reconstruct original healthy vessel: (
a
)seg-
mented clinical image of vasculature depicting IA; (
b
) removal of section containing IA;
(
c
) a Frenet-Frame is constructed along a curve
c
(s)
between the upstream and downstream bound-
aries of the segment containing the IA that was removed; (
d
) methodology to smoothly morph the
inlet boundary into the outlet boundary along
c
;(
e
) reconstructed healthy vessel
The hypothetical healthy geometry is reconstructed by using the Frenet-Frame to
propagate a closed curve in the
N
-
B
plane along
c
such that the upstream boundary
smoothly morphs into the downstream boundary. This approach takes into account
the natural tortuosity of the artery. The vector equation of the reconstructed healthy
section of arterial surface
r
(t,θ)
,
θ
∈[
0
,
2
π)
can be expressed as
=
+
l
(t,θ),
(12.3)
where
l
(t,θ)
represents the position vectors of points on the boundary in the
N
(t)
-
B
(t)
plane along
c
.
l
(
0
,θ)
and
l
(
1
,θ)
are determined from the known posi-
tion vectors of the upstream and downstream boundaries and we choose
l
(t,θ)
to be
a linear combination of these:
l
(t,θ)
r
(t,θ)
c
(t)
=
(
1
t
l
(
1
,θ)
(
N
cos
θ
B
sin
θ).
(12.4)
This novel reconstruction method is applied to 22 clinical cases depicting sidewall
IAs. Figure
12.2
illustrates the application of the approach to 20 (segmented) clinical
cases; the geometry of the IA is depicted in light blue whilst the geometry of the
reconstructed segment of healthy artery is in depicted in dark blue.
−
t)
l
(
0
,θ)
+
+
12.2.1.1 Computational Fluid Dynamics
The methodological approach to solve the hemodynamics proceeds as follows. The
geometry of the artery without IA is imported into ANSYS ICEM (ANSYS Inc.,