Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
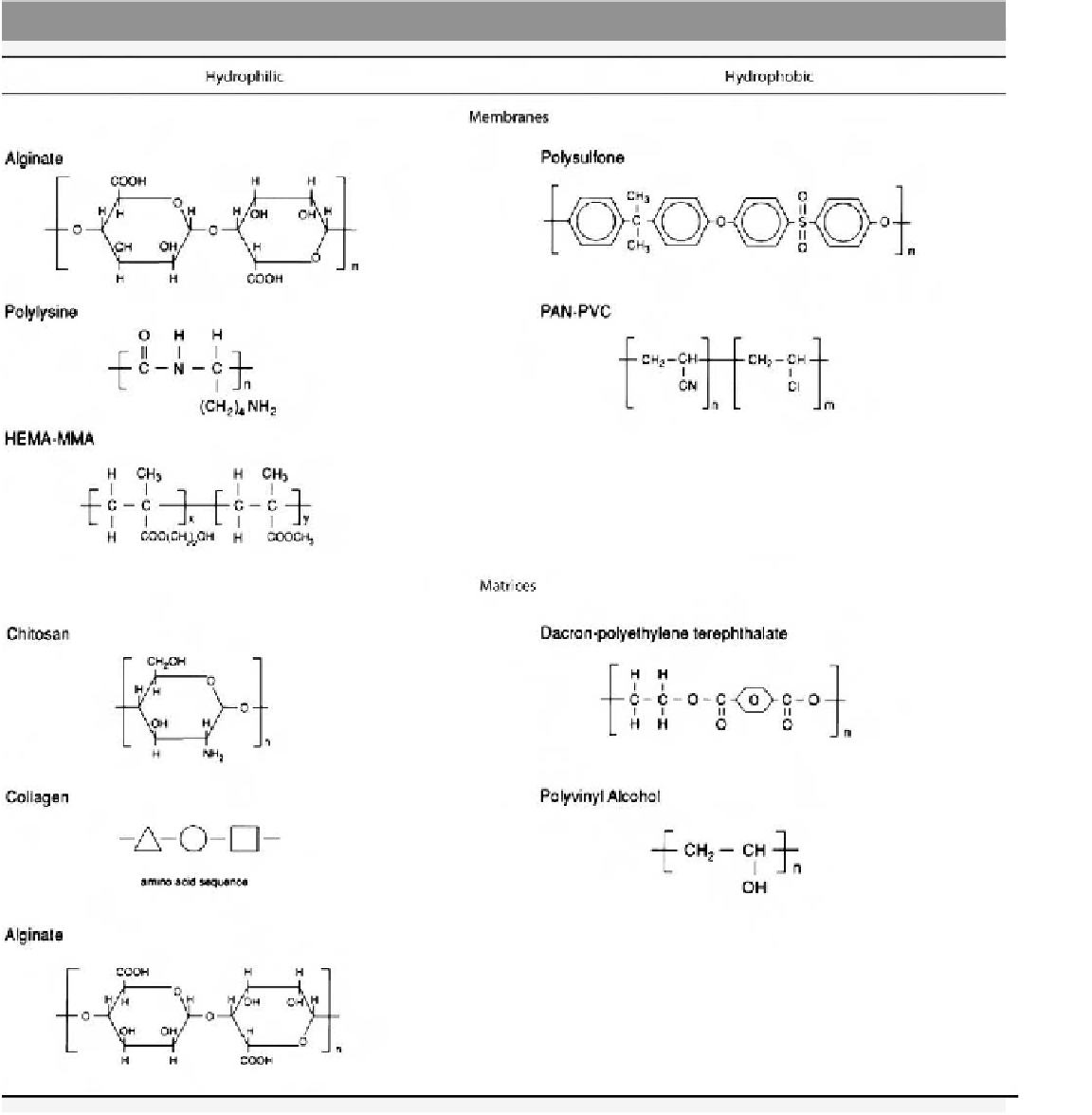
Table 7.1.3-1 Materials commonly used in encapsulation
inversion process: most common are foamlike or trabec-
ular structures. Outer surface morphology is generally
characterized as rough (microgeometries
>
2
m
m) or
smooth. Implanted into a host tissue site, rough surface
will frequently evoke a significant host fibrotic reaction,
whereas smooth surfaces will evoke a relatively mild re-
action. In some cases, a vascularized host reaction can
actually improve encapsulated device viability, by pro-
viding nutrients and oxygen to the perimembrane region.
Matrices
The second component of an immunoisolation device is
the internal matrix. Hydrogels and solid scaffolds have