Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
constantly updated. Access to this database gives users
a self-contained and mobile version of the system that
can be used in the event of catastrophic failure of the
system hardware or network hardware or in the event of
a crisis that removes the users from direct access to the
hospital network.
One of the most important features of the BMD is
that it reformats information from the ADT system and
presents it to the clinical user in a more ''user-friendly''
and process-oriented manner. Dynamic and interactive
graphical presentations of data are used extensively.
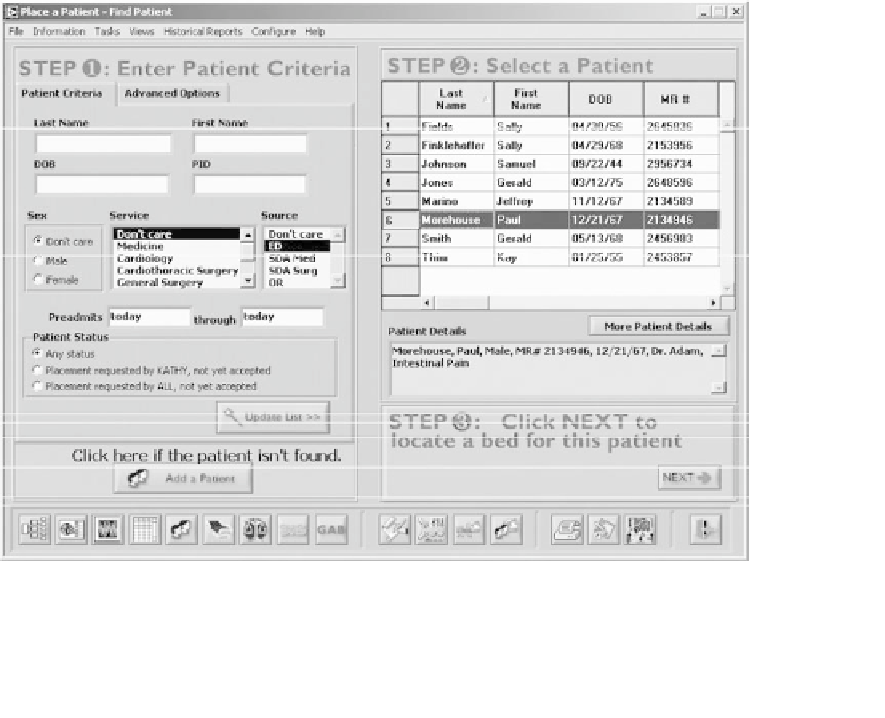
Figure 5.5-4
illustrates the way in which all of the pa-
tients from a given admitting source, such as the ED, can
be displayed and selected from a dynamically sortable
''smart table.''
Hospital beds are classified as having predefined ''at-
tributes,'' such as being ''monitored'' or being assigned to
the ''surgery'' service. The needs of patients are similarly
described with attributes, such as ''monitor required'' or
''scheduled for surgery.'' As illustrated in
Figure 5.5-5
,
the BMD helps to find those available beds in the hospital
that meet the specific needs of a patient by guiding the
clinical staff through a set of process screens that per-
form the match.
Decisions for patient placement can be centralized or
decentralized. The dashboard allows proper communication
between the appropriate parties. Status of decisions is
automatically tracked, and a monitoring process can
detect and notify key stakeholders of any process delays.
Admitting or emergency departments can be automati-
cally notified of decisions, if appropriate. Reporting of
information is provided by online screen views of data
tailored to the needs of a particular class of system user.
Unit personnel can view either detailed information or
summary roll-ups about their patients.
Figure 5.5-6
il-
lustrates ways in which patient information can be
viewed in a dynamic and interactive floor-plan mode.
Administrators and program directors can view data
over a wider scope that encompasses multiple units,
services, or physicians. An example of a summary report
is shown in
Figure 5.5-7
.
A key feature of this system is its use of ''Intelligent
Agents.'' These online agents, as shown in
Figure 5.5-8
,
are constantly monitoring and analyzing patient and
census information, and they have the ability to detect
key system situations, such as high census in a unit (i.e.,
no available beds), excessive ED placement time for
a particular patient, or delays in responses to placement
requests.
The BMD allows users to run real-time queries and re-
ports on current and future hospital census (
Figure 5.5-9
).
These reports are stratified by inpatients, outpatients,
Figure 5.5-4 Find Patient: This screen is primarily used to request a bed for a patient. The user first enters various criteria to identify
the patient. The system then displays all of the patients who meet the specified criteria. Finally, the user selects the patient in question and
presses ''NEXT'' to move to another screen, where an available bed is located and requested.