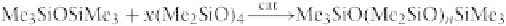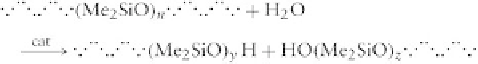Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 3.2.3-4 The Basic Steps in Silicone Polymer Synthesis
very long, viscous chains that are subsequently reduced in
length by the addition of terminal groups provided by the
endblocker, which is slower to react. This reaction can be
described as follows:
The cyclic trimer (Me
2
SiO)
3
has an internal ring
tension and can be polymerized without reequilibration
of the resulting polymers. With this cyclic, polymers
with narrow molecular-weight distribution can be pre-
pared, but also polymers only carrying one terminal
reactive function (living polymerization). Starting from
a mixture of different ''tense'' cyclics also allows the
preparation
or, in shorthand notation:
of
block
or
sequential
polymers
(Noll,
1968).
Linears can combine when catalyzed by many acids or
bases to give long chains by intermolecular condensation
of silanol terminals (Noll, 1968; Stark
et al.
, 1982).
where
n ¼
4
x
(theoretically).
The ratio between D and M units will define the av-
erage molecular weight of the polymer formed.
Catalyst removal (or neutralization) is always an
important step in silicone preparation. Most catalysts
used to prepare silicones can also catalyze the de-
polymerization (attack along the chain), particularly at
elevated
temperatures
in
the
presence
of
traces
of
water.
It is therefore essential to remove all remaining traces of
the catalyst, providing the silicone optimal thermal
stability. Labile catalysts have been developed. These
decompose or are volatilized above the optimum poly-
merization temperature and consequently can be elimi-
nated by a brief overheating. In this way, catalyst
neutralization or filtration can be avoided (Noll, 1968).
A distribution of chain lengths is obtained. Longer
chains are favored when working under vacuum and/or at
elevated temperatures to reduce the residual water
concentration. In addition to the polymers described
above, reactive polymers can also be prepared. This
can
be
achieved
when
reequilibrating
oligomers
or