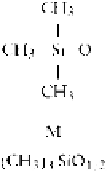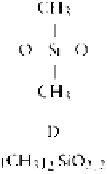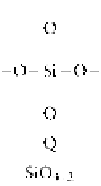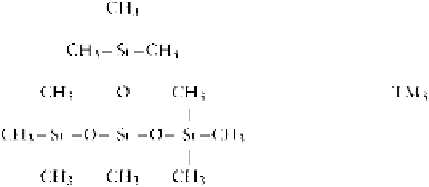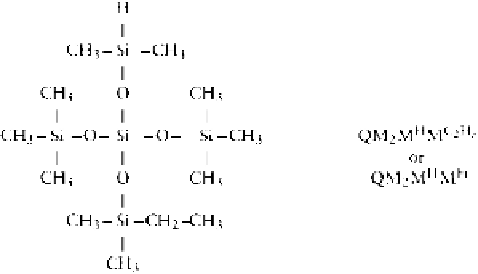Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Preparation
Table 3.2.3-2 Shorthand notation for siloxane polymer units
Silicone polymers
The modern synthesis of silicone polymers is multifac-
eted. It usually involves the four basic steps described in
Table 3.2.3-4
. Only step 4 in this table will be elaborated
upon here.
Polymerization and Polycondensation.
The linear [4]
and cyclic [5] oligomers resulting from dimethyldi-
chlorosilane hydrolysis have chain lengths too short for
most applications. The cyclics must be polymerized, and
the linears condensed, to give macromolecules of suffi-
cient length (Noll, 1968).
Catalyzed by acids or bases, cyclosiloxanes (R
2
SiO)
m
are ring-opened and polymerized to form long linear
chains. At equilibrium, the reaction results in a mixture
of cyclic oligomers plus a distribution of linear polymers.
The proportion of cyclics will depend on the substituents
along the Si-O chain, the temperature, and the presence
of a solvent. Polymer chain length will depend on the
presence and concentration of substances capable of
giving chain ends. For example, in the KOH-catalyzed
polymerization of the cyclic tetramer octamethylcyclo-
tetrasiloxane (Me
2
Si
O
)
4
(or D
4
in shorthand notation),
the average length of the polymer chains will depend on
the KOH concentration:
Table 3.2.3-3 Examples of silicone shorthand notation
xð
Me
2
SiO
Þ
4
þ
KOH /
ð
Me
2
SiO
Þ
y
þ
KO
ð
Me
2
SiO
Þ
z
H
A stable hydroxy-terminated polymer, HO(Me
2
SiO)
z
H,
can be isolated after neutralization and removal of the
remaining cyclics by stripping the mixture under vacuum
at elevated temperature. A distribution of chains with
different lengths is obtained.
The reaction can also be made in the presence of
Me
3
SiOSiMe
3
, which will act as a chain end blocker:
where represents the main chain.
The Me
3
SiOK formed will attack another chain to
reduce the average molecular weight of the linear poly-
mer formed.
The copolymerization of (Me
2
SiO)
4
in the presence
of Me
3
SiOSiMe
3
with Me
4
NOH as catalyst displays
a surprising viscosity change over time (Noll, 1968). First
a peak or viscosity maximum is observed at the beginning
of the reaction. The presence of two oxygen atoms on
each silicon in the cyclics makes them more susceptible
to a nucleophilic attack by the base catalyst than the
silicon of the endblocker, which is substituted by only
one oxygen atom. The cyclics are polymerized first into